This article will help you to make comparison among radio, TV and print media.
Radio Vs. TV Vs. Print Media:
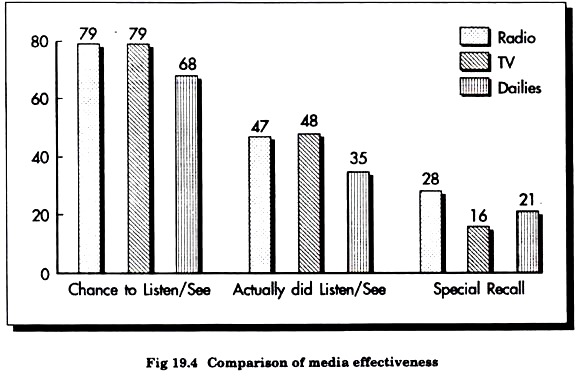
The advent of electronic communication has resulted in a veritable media explosion. New technologies are constantly being developed. But the radio still is an effective medium which reaches the rich as well as poor, to both literate and illiterate at the lowest possible cost.
One of the major advantages of radio is its ability to reach people in their work place. It is a localized medium that at the same time can cover large audiences. For the consumers with monthly household incomes up to Rs. 750 and then between Rs. 750 and Rs. 1,500, radio listenership is higher than reading newspapers & magazines.
The India readership survey (IRS) 95, which covers both urban and rural areas, says that reach of both press and radio is 22% all India.
The over shrinking ad budgets and increased competition for hard won consumer money, the advertiser wants to be sure that his message will be heard and remembered by the people he wants to reach. So when buying the best media, two qualities determine whether an appeal will ultimately accepted or rejected. First is credibility of the source and another is likeability.
The Credibility of the Source Depends on:
(a) The perceived expertise of the source or the extent to which the source is seen as bright and knowledgeable.
(b) The perceived trust worthiness of the source.
The likeability means that the more attractive the source, the more persuasive the appeal. One of the greatest strengths of radio is its flexibility. Changes to the script can be made very quickly and when marketing conditions change, one can react instantly on radio.
Radio effects and enriches what is understood through exposure to press or TV. When used in combination, it multiplies the effect of other media to produce a richer, more detailed advertising message by adding weight to scheduling.
With the launch of FM and privatization, economic liberalization, more hours of programming, more stations an coming up. And so, more intimate, personal ads are making their way between the advertiser and listener, which will give more value to the advertiser.
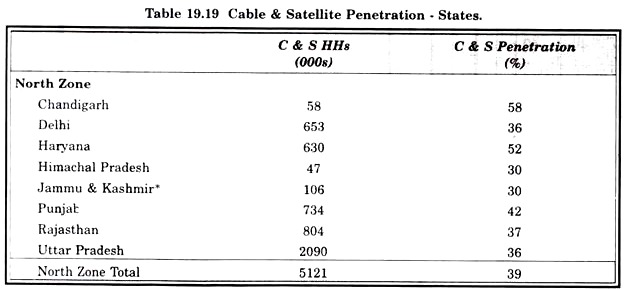
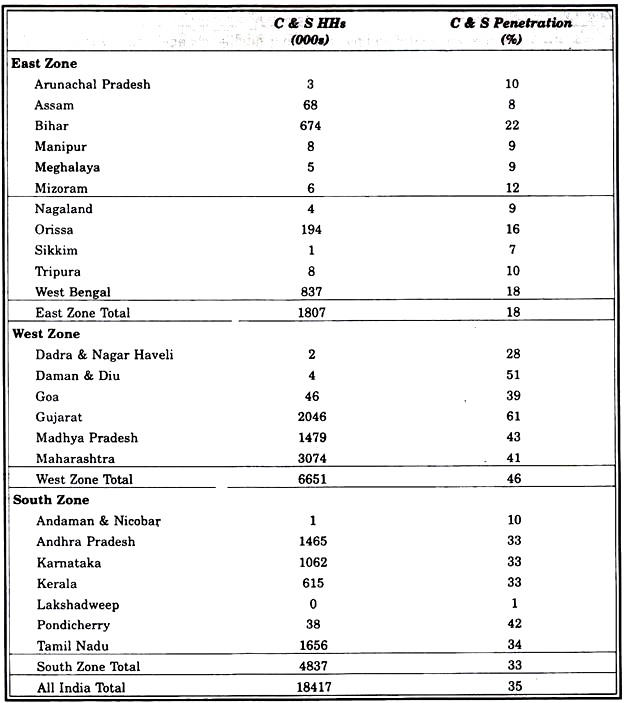
Cable and Satellite Television:
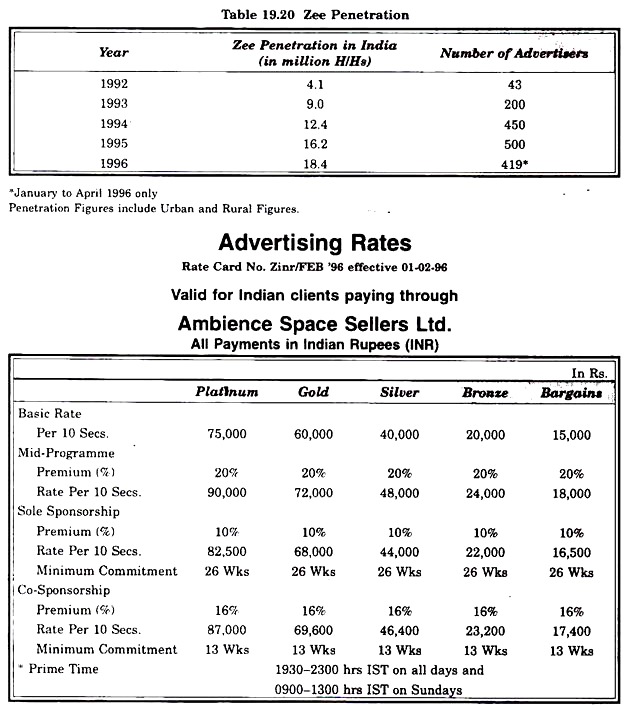
Zee TV:
It is South Asia’s most successful and popular Hindi satellite channel, reaches over 18 million homes in India, 5 million homes in Pakistan, Bangladesh and the middle east. The Zee viewer is largely more affluent, more educated than the average TV viewers and also has a higher spending capacity.
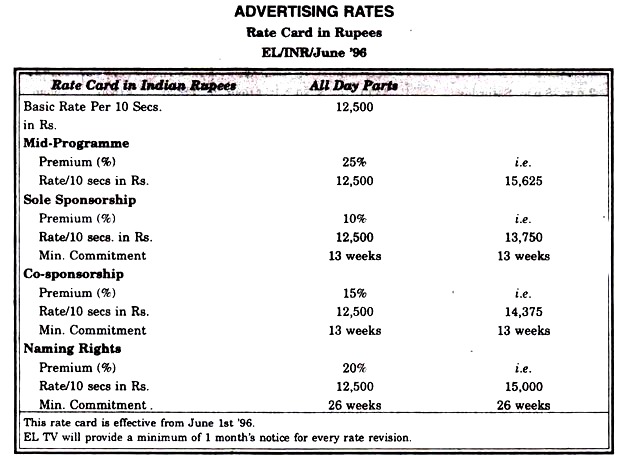
El-TV:
El-TV viewers are more educated and affluent & have a greater propensity to spend. Nearly 50% of the viewers are in the 15-35 years age group.
Sony Entertainment Television:
Sony Entertainment Television was launched in August, 1995 covering the Indian ocean. The rate card for commercials is as follows:
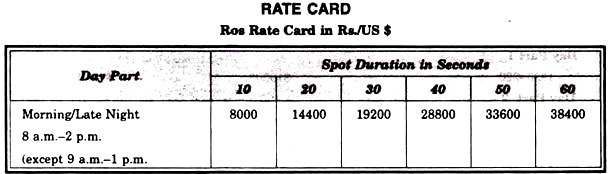
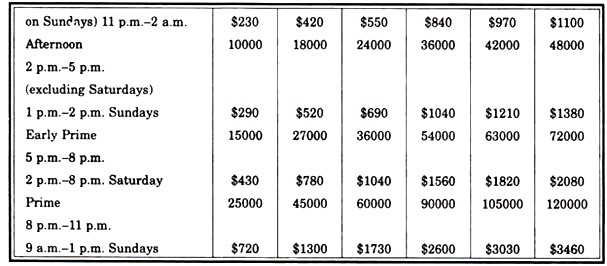
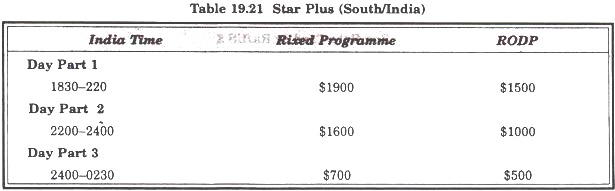
Star TV:
Star TV is the first and only Pan-Asian Satellite television network. Its channel reaches to nearly 54 million households across 53 countries.
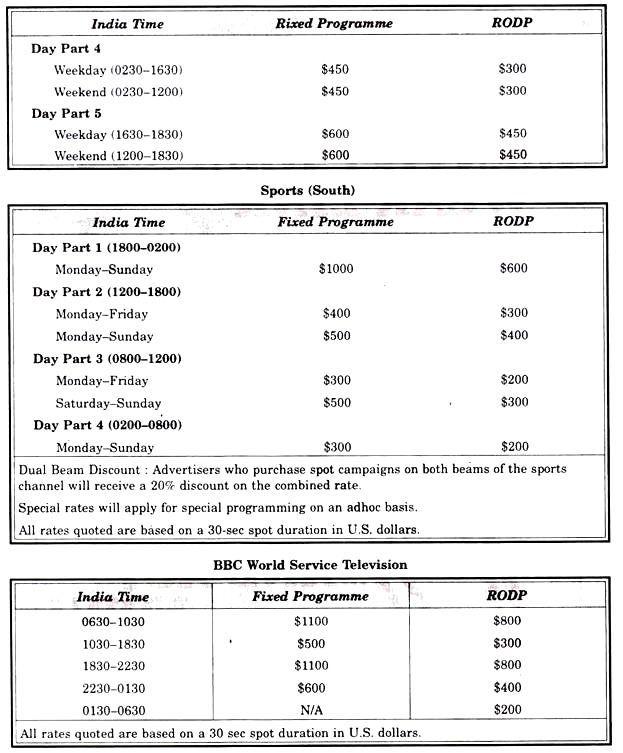
Rate Class:
(a) Run of schedule rate (code ROS) – Subject to availability, these sports are rotational within the specific day and channel and are subject to preemption.
(b) Fixed time Bond rate (code FB) – Subject to availability, these sports are rotational within a pre-selected four hour time band.
(c) Run of day part (code RODP) – These sports are placed at star TVS discretion within the day part parameters.
(d) Fixed hour rate (code FJI) – Subject to availability, these sports are fixed within the specific day channel and hour.
1. Special programme and sponsored programme spots preempt regular programme spots.
2. Programme Sponsorship will be subject to negotiation.
3. Special rates will apply for special programmes on an adhoc basis.