This article throws light upon the five main gateways to effective communication. The gateways are: 1. Interpersonal Trust 2. Effective Listening 3. Proper Feedback 4. Non-Verbal Cues 5. Non-Directive Counseling.
Effective Communication: Gateway # 1.
Interpersonal Trust:
It is impossible to communicate effectively without interpersonal trust. A subordinate will not be able communicate freely with his manager unless he trusts the latter. By being fair, open and receptive to new ideas, top managers can create a favorable atmosphere for developing interpersonal trust.
Effective Communication: Gateway # 2.
Effective Listening:
Listening is one of the most essential elements of effective communication. A message can never be conveyed effectively unless the receiver is attentive and listens to what is being said. The listener should be open minded in order to understand the correct meaning of a message. According to a research study, these are the ten prerequisites for effective listening.
(i) Judging the content of the message, but not the weaknesses of the speaker.
(ii) Avoiding premature evaluation.
(iii) Looking for the central idea.
(iv) Being flexible and not expecting the message to follow a fixed pattern.
(v) Concentrating on the message.
(vi) Being mentally alert to grasp the meaning of the message.
(vii) Practicing active listening.
(viii) Having an open mind.
(ix) Trying to benefit from one’s own rapid ‘thought process’ rather than ‘talk processes’ of the speaker.
Effective listening helps managers improve their relationships with their subordinates. It also helps them give feedback and provide non-directive counseling.
Effective Communication: Gateway # 3.
Proper Feedback:
Feedback enables the sender to assess the effect of a message transmitted to the receiver. Both giving and receiving feedback are important aspects of management. To be effective, the feedback provided by managers should be descriptive, specific, and directed towards changing specific behaviors. When receiving feedback, managers should be opening minded.
They should be able to handle both positive as well as negative feedback. While receiving negative feedback, managers should ask for clarification and examples about points which seem ambiguous or unclear. They should also avoid acting defensively.
Nowadays, many organizations encourage their customers to give feedback regarding their products or services. This helps organizations make improvements in their products or services.
Effective Communication: Gateway # 4.
Non-Verbal Cues:
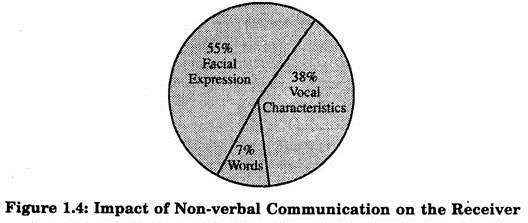
Another important prerequisite for effective communication is an awareness of and sensitivity to non-verbal cues in communication. The following pie charts (Figure 1.4), based on a research study, and reveal the significance of non-verbal communication.
According to this graph, only 7 percent of a receiver’s response is determined by the verbal content of a message, while 38 percent of the response is determined by the speaker’s vocal characteristics (tone and tenor of the voice) and 55 percent of the response is determined by the speaker’s facial expressions.
The above figure reveals the enormous impact of non-verbal communication on the receiver. Non-verbal cues include body posture, eye contact, distance from the receiver, voice inflection, rate of speech, gestures, emphasis of particular words, silence, etc.
An awareness of non-verbal cues helps managers become sensitive to the needs of their subordinates. Such awareness helps managers assess the current state of their interpersonal relationships with subordinates and manage them effectively.
Effective Communication: Gateway # 5.
Non-Directive Counseling:
In non-directive counseling, the manager helps the employee examine his own ideas, feelings and attitudes about a problem. Non-directive counseling can be done by holding an interview with the employee.
In a non-directive counseling interview, a manager should:
(i) Be attentive and friendly
(ii) Raise appropriate questions
(iii) Be tactful and enable the employee to think through the problem clearly
(iv) Create an atmosphere of privacy to ensure that the employee can communicate freely
(v) Be a patient listener to help the employee to express his emotions freely
(vi) Encourage the employee to do some introspection.