Here is a compilation of essays on ‘Marketing Audit’ for class 11 and 12. Find paragraphs, long and short essays on ‘Marketing Audit’ especially written for school and college students.
Essay on Marketing Audit
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Concept of Marketing Audit
- Essay on the Aim of Marketing Audit
- Essay on the Nature and Scope of Marketing Audit
- Essay on the Importance of Marketing Audit
- Essay on the Role of Marketing Audit in Business
- Essay on the Limitations of Marketing Audit
- Essay on the Aspects of Marketing Audit
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Essay # 1. Concept of Marketing Audit:
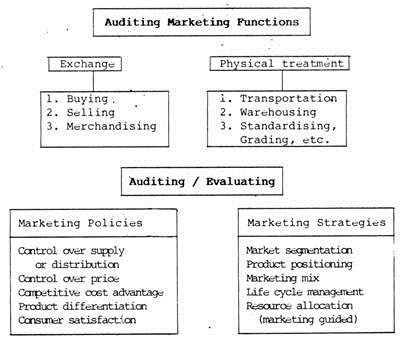
Marketing as a discipline and as a component of the total business operations covers two broad aspects: marketing functions and marketing policies. The first aspect covers all those efforts and activities which are necessary for the journey of goods from the producer to the ultimate consumer.
The-second aspect deals with policies and strategies for achieving success in the competitive market place through consumer satisfaction and services.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Thus, the marketing audit scenario can be outlined in charts below:
The marketing audit involves the assessment of the business environment, both internal and external -in relation to the past, present and projected future in which an organisation operates.
This audit evaluates the strengths and weaknesses, and opportunities and threats (SWOT) of each of the product lines in relation to the markets and consumers.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It consists of three parts:
1. product factors analysis,
2. product performance analysis, and
3. business operations audit.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
These are explained below:
1. In marketing audit, the product factors analysis is a qualitative evaluation of each significant product line and its markets. It is done by a comparative evaluation between the line of business and all competitive products. The findings of this analysis are interpreted in terms SWOT far each product line.
This is done in the following six steps:
Step 1: Marketing:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(1) Current size and share of market served.
(2) Annual compound growth rate of market served for a period of few years.
(3) Internal sales growth rate compounded for the past few years.
(4) Demand forecast and elasticities.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Step 2: Competition:
(1) Competitors including the entity accounting for the largest sales in the market served.
(2) Relative market share compared to the largest competitor.
(3) The changes in the market share position for the last few years — Own Vs. Competitors.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Step 3: Technical:
(1) State of the arts and sciences.
(2) Entity’s own technical skills.
(3) Relative technical position compared to the competitors.
(4) Technical advantages possessed by the competitors.
Step 4: Operational:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(1) Gross margin.
(2) Productivity growth rate.
(3) Average age of existing producing equipment.
(4) Specific production advantages possessed by the entity over the competitors.
Step 5: Financial:
(1) Cash flow.
(2) After-tax return on sales.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(3) Return on assets employed.
(4) Capacity utilisation.
(5) Contribution per product line.
Step 6: Final:
(1) Reviewing past performance and future potentials.
(2) Ascertaining and assessing SWOT.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. In marketing audit, the product performance analysis is a quantitative of each significant product and its markets. It starts with a critical estimate of the measures of performance, during the past few years. Historical performance data are used for this exercise.
In this quantitative assessment, the specific data categories included are: product identification, product life, market size, market growth rate, sales volume, after tax earnings, after-tax cash flow, etc. With these information, performance measures for each year are calculated. They usually include: market share, annual product sales growth, return on sales, return on assets, assets turnover.
3. The business operations audit, the last part of the marketing audit, reviews the, overall operations of an enterprise from the stand points of functional operations such as warehousing, transportation and traffic services, selling, etc., and general management.
To conclude, the market audit is the window through which we can best view the future and develop strategies which are the essence of planning. It provides the means to determine goals which will facilitate achievement of maximum results from the business. It helps to identify the actions necessary for developing the strategies and tactics to be employed in achieving the desired goals.
Essay # 2. Aims of Marketing Audit:
The basic purpose of marketing audit is to identify present and potential marketing problems and find out their possible remedies. It is a search for existing and potential opportunities, to apply the factors which create strength in one marketing activity’ to others.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In this way, it serves the following purposes and objectives:
(i) To locate, existing weakness and to pinpoint current problem and their sources.
(ii) To search existing marketing weakness as veil as future problems.
(iii) To identify current problems and determine their cause, but at the same time it probes for incipient problems those just beginning or likely to emerge.
(iv) To search market opportunities which had previously been over looked or which have only recently emerged.
If brief, the identification of marketing problems and possible remedies is, however, only one of the purposes of the marketing audit. The audit is, in addition, concerned with identifying, in particular, strengths of the marketing operation.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Essay # 3. Nature and Scope of Marketing Audit:
Like other types of evaluation, marketing audit is an examination of all the marketing activities in order to ascertain their effectiveness. It is basically a re-examination and evaluation of marketing objectives and policies.
It is an appraisal not only of a company’s marketing programmes but also of the framework which has given the programme its direction, structure, and shape. It is primarily concerned with identifying the strength and weakness of the total marketing operation.
According to the eminent authors like Philip Kotler and otters, the marketing audit has the following characteristics which explain its nature and scope from the broader perspectives:
1. It makes a comprehensive study and evaluation of all the marketing operations of a business entity, not just a few trouble spots.
2. It involves the study of the marketing environment of an organisation, its internal marketing system, and specific marketing programmes, etc.
3. It is an analytical inquiry of marketing operations, objectives, policies, and their effectiveness.
4. It is not only analytical in nature, but also a diagnostic tool. It is concerned with the present as well as future. It is a kind of research into the existing weaknesses and into those which may crop up in future.
5. It is an independent and intelligent analysis which reflects the goals and their achievement along with their effectiveness.
6. Marketing audit can be conducted in six ways:
(a) Self audit,
(b) Audit from across,
(c) Audit from above,
(d) Company auditing office,
(e) Company task force audit, and
(f) Outsider audit.
Self-audit is useful when managers use a checklist to rate their own operation. For marketing audit to be successful and effective experience, objectivity, and independence are the basic requirements.
7. Philip Kotler is of the view that marketing audit is initiated only after sales have turned down, sales force morale has fallen and other company problems have occurred. A periodic audit can benefit companies in good health as well as those in trouble.
8. It is preventive as well as curative in nature. It is relevant not only to sick industries, but it also guarantees healthy aid successful functioning of the firms.
Essay # 4. Importance of Marketing Audit:
Auditing is not new in the business world. The examination and review of financial statements have been going on for a long-time in business.
However, the issues like the increasing business intricacies, competition buying market, increase in the cost of production and distribution, and the rapid pace of change in our modes of living have rendered it vital that marketing aspects of business should be examined thoroughly and adopted according to the changing marketing environment.
In other words, business today has become very complicated and it operates in a very dynamic atmosphere. The planning and execution of marketing strategies and programmes are running in a process of flux. In such complex circumstances, it; is very difficult for any marketing executive to predict about the future market trends.
Because of the growing marketing complexities in modern business, no businessman can depend on auditing of financial statements alone for ascertaining the reality and marketing effectiveness of his business. This limitation of auditing has given rise to certain new dimensions of auditing in which marketing audit is important.
Although the concept of audit is not new to business management yet marketing audit is relatively a new term. It is an innovation in the marketing field providing an effective measure to check all the marketing activities.
Essay # 5. Role of Marketing Audit in Business:
All business organisations operate under the dynamic environment characterised by keen competition, research, innovations, product diversification, government interference, large scale production and creation of complex organisation.
In this dynamic and continuously changing position, the growth and survival of most companies depend primarily upon the success of their marketing operation, because the role of marketing activities among all business activities has an overriding importance in the shaping of a firm’s destiny. Therefore, the regular evaluation of all marketing activities has become essential for a modern business.
Today all marketing executives know that they operate in a highly fluid, environment. They are fully aware that unceasing change is the salient characteristic of their company’s marketing situation.
They recognise that there are constant and continuous changes, sometimes even abrupt and dramatic in size, competition, market composition, distribution, consumer tastes, preferences, habit, technology, etc.
Therefore, the timely adjustment between marketing environment has become essential for modern business. Unless the marketing operation is revamped in tine, and unless the objectives, policies, methods, procedures, personnel and organisation are once again combined into a carefully articulated plan, the drift will certainly precipate a company crisis.
Essay # 6. Limitations of Marketing Audit:
As marketing audit deals with human nature and its tendencies, hence the human weakness produces hindrances in this audit. Marketing audit has to face the problem of opposition because nobody likes to be subjected to evaluation. The auditor will have to face people with different nature.
Naturally the auditor will require a lot of time to study it. Envy, animosity, nepotism and such other realities of human nature renders the work of the auditor almost insurmountable. Marketing audit normally tends to user in change in the established order.
But who wants the change, because it may affect the hierarchy of business institution. Lastly, it is based on qualitative facts which are very difficult to ascertain. Such an auditor must be few and far between.
Essay # 7. Aspects of Marketing Audit:
The following aspects of an organisation are generally addressed in the marketing audit.
These are discussed in brief:
1. Evaluation of Marketing Planning:
In it, we study how a thing is produced and ultimately how it is made available to consumer, and even certain activities thereafter. In other words, the whole gamut of problems from production to consumption come under this head.
2. Review of Marketing Control:
Here we analyse the procedure of exercising control and other techniques in marketing.
The following are the basic control techniques in marketing:
(a) Strategic control techniques
(b) Annual plan control techniques
(c) Profitability control techniques
3. Review of Marketing Information System:
It includes horizontal as well as vertical communication system.
4. Review of Different Marketing Operation:
The following points are included here:
(a) Consumer motivation and behaviour
(b) Market, segmentation
(c) Sales forecasting
(d) Marketing research
(e) Marketing decision making (regarding product, price, place and promotion.)
According to Kotler, the examination of the following six components of the company’s marketing situation are included in marketing audit:
(i) Marketing Environment Audit:
In it, major macro environment forces and trends in the key components of the company’s task environment (Markets, customers, competitors, distributors and dealers, suppliers and facilitators) are analysed.
(ii) Marketing Strategy Audit:
In it, the company’s marketing objectives and marketing strategy are reviewed to appraise how well these are adopted to the current and forecasted marketing environment.
(iii) Marketing-Oganisation audit:
It is related to evaluate the capacity of the marketing organisation implementing the necessary strategy for the forecasted environment.
(iv) Marketing Systems Audit:
This audit involves examining the quality of the company’s systems for analysis, planning and control.
(v) Marketing Productivity Audit:
In it, the profitability of different marketing entities and cost effectiveness of different marketing expenditures are examined.
(vi) Marketing Function Audit:
This audit consists of in depth evaluation of major marketing mix components, namely product price, distribution, sales force, advertising promotion and publicity.