After reading this essay you will learn about:- 1. Introduction to Marketing 2. Definition of Marketing 3. Principles 4. Functions 5. Cost 6. Process 7. Orientations.
Contents:
- Essay on the Introduction to Marketing
- Essay on the Definition of Marketing
- Essay on the Principles of Marketing
- Essay on the Functions of Marketing
- Essay on the Cost of Marketing
- Essay on the Process of Marketing
- Essay on the Orientations of Marketing
Essay # 1. Introduction to Marketing:
Marketing has its origins in the fact that man is a creature of needs and wants. Needs and wants create a state of discomfort in persons and they tend to get objects (i.e., products) those satisfy these needs and wants. For example in the months of summer, if in an area, ice is not freely available or when eatable tend to get distasted in summer, persons feel discomfort and they satisfy their needs by purchasing a refrigerator.
The word marketing has been derived from Market which may be looked upon as an arena for potential exchanges, i.e., a place where products can be exchanged by money or anything else, e.g., a political candidate offers promises of good government to a voter market in exchange for their votes.
There are need markets, product markets, demographic markets, geographic markets, etc.
The size of the market depends upon the number of persons who have both:
(i) An interest in the product; and
(ii) Are willing to offer something (say money) in exchange of the product.
Essay # 2. Definition of Marketing:
The concept of markets leads to the concept of marketing. Marketing means working with markets, i.e., trying to actualize potential exchanges for the purpose of satisfying human needs and wants. Marketing, therefore, may be defined as human activity directed at satisfying needs and wants through exchange processes; examples of human needs and wants are food, water, clothing, education and other services. Marketing in its broad meaning includes the policy, techniques and methods necessary for selling and distribution.
Without marketing function, goods and services cannot be sold. Marketing is the total commercial and support activities of any enterprise to effect sales of company end products or services. Marketing involves planning and execution of all aspects and activities of a product so as to exert optimum influence on the consumer to result in maximum consumption at the optimum price and therefore producing the maximum long term profit.
Essay # 3. Principles of Marketing:
The five basic principles of sound marketing are described below:
1. Marketing must provide a means of classifying, assessing and integrating information relevant to a business.
2. It must provide a sound base for thinking about and studying business problems and provide methods to draw correct conclusions which form basis for action.
3. Marketing must be able to explain, predict and control the process it employs.
4. Marketing must use analytical methods such as O.R., Statistics, Computer Technology, etc., to solve its problems.
5. Marketing should allow the derivation of a number of its principles adaptable to any particular business.
Essay # 4. Functions/Objectives of Marketing:
The functions, aims and objectives of marketing are:
(i) To give direction and purpose to the marketing division as a whole as well as to its various departments.
(ii) To place present activities in perspective.
(iii) To discipline various future activities.
(iv) To place tactical plans correctly in the strategic setting.
(v) To set growth targets.
(vi) To establish the organisation and the methods which will be required.
Essay # 5. Cost of Marketing:
Marketing costs are generally high. The study of marketing of wheat, rice and cotton in India indicated that 50 to 60% of the total cost accounted for the marketing costs.
Reasons for high cost of marketing:
(i) There is a big gap between the points of production and consumption. This gap is bridged by an army of middle men-both merchants and agents. This results in high cost.
(ii) Moreover, society has also accepted to pay high prices in view of the valuable services that it is getting in return, from the above mentioned marketing system.
(iii) The inefficiency that creeps in various marketing functions and segments due to presence of inefficient and incompetent men, also results in higher cost of marketing.
To reduce marketing costs:
(i) Un-necessary crowd of middlemen should be avoided.
(ii) Development of chain stores, multiple shops and departmental stores are the innovations of marketing men to avoid middlemen.
(iii) People in marketing line should be qualified and experts.
(iv) Cooperatives should be developed to provide better services to customers.
(v) Government should provide fast and reliable transportation systems (railways, roadways etc.) and communication systems.
Essay # 6. Process of Modern Marketing:
Marketing is the process of discovering and translating consumer’s wants into products and services. According to modern marketing concept, marketing starts with the product-idea and ends with customer satisfaction.
Marketing process covers marketing functions as well as marketing agencies or channels of distribution. Marketing process brings together producers and consumers. Each producer (or seller) has certain goals in making and marketing his products.
An exchange (or transaction) takes place when market offering is acceptable to the consumer who is prepared to give something of value (i.e., money) in return against the product he wants to buy. In the process of exchange, both (seller and consumer) give up something and both gain something in return.
The seller gets the profit and the consumer gets utility (of product) or individual satisfaction. Thus market mechanism brings together a willing seller and a willing and informed buyer together for mutual gain.
The marketing process is influenced by:
(1) Competition,
(2) Government rules and policies, and
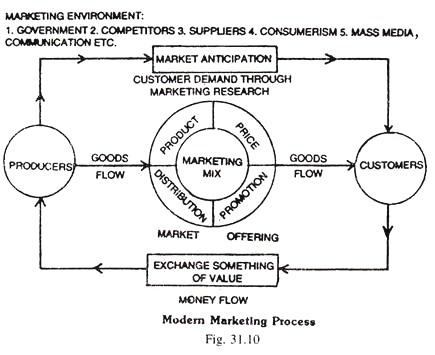
(3) Mass media or communication etc. (refer Fig. 31.10).
Marketing environment (Fig. 31.10) affects both producer and consumer.
The marketing process involves three major activities:
1. Concentration.
2. Dispersion.
3. Equalisation.
The products which have been concentrated at the central markets are dispersed from the producer toward the consumer. The process of equalisation involves proper adjustment of supply at all centres of distribution in the light of current market conditions. The producers carry out market anticipation work. They study customer demand through marketing research.
Marketing research is the starting point in the marketing process to ascertain and identify customer needs and desires through market analysis and investigation, Resources of men, money, materials and management are employed in the marketing system to perform marketing functions and thereby achieve the satisfaction of customer demand.
Producers manufacture a number of products. Then, marketing is a matching process by which the producer provides a marketing mix (product, price, promotion and physical distribution) that meets consumer demand; thus products/goods flow from producer to the customers. When the customers buy the products, the flow of money takes place from the customer to the producers.
Essay # 7. Orientations in Marketing:
Marketing is a philosophy as well as a technology. As a philosophy, it guides whether to produce something or not to produce. As a technology it decides what should be produced, how and when products could be most effectively distributed among the customers. Hence, a producer, always, has to face the changing (mood or) conditions of the human behaviour.
As a result of the changing human behaviour, the evolution of marketing concept had the following orientations:
(1) Exchange oriented marketing:
In the early period of human history, every human being or a family had to gather their food by hunting or so and they were self-sufficient. At this stage marketing was totally absent. As the time passed, man started producing more than what he could consume.
Somebody produced wheat, other fruits, so they mutually exchanged their surplus with each other. This was nothing but barter system. The (surplus) products used to be brought at central places (called local markets) for the purpose of exchange. This was the first stage in the evolution of marketing.
(2) Product oriented marketing:
This stage came after the Industrial revolution when there was a shift from agriculture to industry and the means of transport and communications had also somewhat developed. The importance of marketing concept was realised, however, no serious efforts were made to satisfy the wants of the consumers.
It was because the product demand usually outstripped the production capacity. This concept of marketing was marked as product oriented because it lay more emphasis on the product rather than on the consumers.
In the product-oriented concept/stage, it is believed that if the product is good and reasonably priced, customer response is bound to be favourable and little marketing effort will be necessary to achieve satisfactory sales and profit.
There was a time, in India, when only two brands of cars that is Ambassador and Fiat were available in the market and (unlike today) the customer had no choice except for to buy this or that. The consumers knew these two brands of cars and therefore no promotion efforts were there on the part of producers of these cars.
(3) Sales-oriented marketing stage (selling concept):
With the passage of time, there was rise in living standards of the customers and the means of transport and communication had developed. These changes compelled to have an organised marketing procedure.
Under sales-oriented approach, it was assumed that the customers will normally not buy enough unless approached through incentive sales promotion, advertising and salesmanship efforts. But, under this concept, no efforts were made to satisfy the particular needs of the customers. In other words, more emphasis was laid on increasing the sales than on customer’s need and satisfaction.
(4) Marketing-oriented approach:
Marketing-oriented approach developed after the sales-oriented stage. In marketing-oriented approach, it is realized that the producer should determine the needs and wants of the customers and deliver the goods accordingly but more effectively and efficiently than its competitors.
The aim of marketing is to know and understand the customer so well that the product (and service) fits him and sells itself. The selling and the marketing concepts are quite often confused. However, selling focuses on the needs of the seller (i.e., the seller’s need to convert his product into cash); whereas marketing focuses on the needs (and satisfaction) of the consumers.
(5) Customer-oriented marketing:
This is a modern philosophy of marketing and it was introduced only after 1950, when production went in excess of demand and the competition became keen. Under this concept, goods are produced to satisfy the needs and wants of the customers. Only such products are brought forward which can satisfy the wants and tastes of the Consumers. Customer-oriented approach is related to the needs of the buyer.
(6) Socially-oriented marketing:
The business enterprise engaged in the marketing process itself is influenced by social environment. It consists of political, economic, social, cultural and technological forces. Marketers have to adapt with these ever-changing environment forces and fulfill the needs and desires of the society or community.
According to socially-oriented concept, marketing is a social activity, because:
(1) Marketing provides new goods and improved services to people in the society, thereby raising the standard Of living of the people,
(2) Marketing provides employment to people, and
(3) Sound marketing decreases the distribution cost and increases the National Income.
In the long run, society monitors the marketing process and controls its effectiveness. The modern business enterprise is called upon to demonstrate simultaneously higher level of economic performance and fulfillment of social responsibility i.e., high level of consumer/citizen welfare and satisfaction.
Marketing process must reflect social awareness and social responsibility in all business enterprises. Then only the survival, growth and prosperity of the marketing units can be assured.