Here is an essay on ‘Online Trading in India’ for class 11 and 12. Find paragraphs, long and short essays on ‘Online Trading in India’ especially written for school and college students.
Essay on Online Trading in India
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Introduction to Online Trading
- Essay on the Online Trading in India
- Essay on the Network Design for Online Trading
- Essay on the Big Two Architectures of Online Trading in India
- Essay on the Online Trading Process
- Essay on the Impact of Online Trading on Securities Market
- Essay on the Problems Relating to Online Trading
- Essay on the Growth of Online Trading in India
Essay # 1. Introduction to Online Trading:
The rapidly advancing technology, particularly the Internet, has drastically changed the social and economic landscapes and every aspect of our daily lives. In the securities industry, the Internet has facilitated on-line trading, changing the way the market works, as well as the way the investors access the market.
Stock exchanges worldwide now conduct a bulk of their business online through brokers and partners, a major shift from the traditional method. In developed countries, almost all exchange transactions are conducted online. The trend has slowly picked up in India and two of the largest exchanges, the national Stock Exchange (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) have been conducting online trade successfully.
Meaning:
“On-line trading” is broadly defined as trading mechanism where investors place orders and confirm trading results via electronic communication channels, such as the Internet, mobile phones, and Personal Digital Assistant (PDA). The whole process of securities transactions, from order placement and routing, order execution, to trade confirmation, is fully automated, thus enabling the investors who have placed orders to confirm their trading results within a few seconds.
Essay # 2. Online Trading in India:
Indian exchanges and brokering houses have been slow to move their transactions online. This has been mainly due to Government regulations. There was initial delay in laying down specifications for creating Closed User Groups (CUGs). The issue was resolved between the DoT and the Finance Ministry around 1998 and soon trade portals like ICICIDirect(dot)com, motilaloswal(dot)com, and smartjones(dot)com came into being.
Connectivity was perhaps the most important technological factor. The cost of leased lines and Very Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT) links has been traditionally very high and the reliability of the links has been low. It also took a long time to commission the links as one had to make an application and wait for a few weeks for the link to be up and running.
Other issues like security, backup and recovery procedural costs were also deterrents. With the entry of private players into the broadband scenario and the government opening up the telecom sector, these issues were resolved. Security solutions and services available in the market have matured and it is cheaper to put a simple backup solution in place.
Indian Stock Exchanges:
The NSE and BSE, largest stock exchanges in the country, handle very large daily trading volumes, support large amounts of data traffic, and have a very large nationwide network. The trading volume figures in both the exchanges are huge. The average daily turnover in the capital markets segment at NSE is around Rs. 9,518 crore and in the derivatives segment, around Rs. 19,375 crore in 2005-06.
The average daily turnover traffic volume is around three million trades per day in the cash segment of NSE and around 50,000 trades per day in the derivatives segment. There are around 13,000 registered users in both segments and an average of around 9500 users, logged in at a time.
Essay # 3. Network Design for Online Trading:
Online exchange needs to be always-on, secure, redundant, and have adequate backup and recovery processes. The basic design objective was to provide fair, equal, and transparent access across all our nationwide locations. An important aspect was to provide connectivity to our trading members as soon as possible.
Satellite technology was a boon as it allowed quicker deployment than leased lines. NSE now has the country’s largest VSAT network with over 3000 VSATs and expects to grow to more than 4000 VSATs soon.
A look at the massive trading volumes and traffic bulk is enough proof of the critical nature of systems. Even a ten minute down during trading hours leads to terrible losses. Hence, network elements like storage, security, backup and recovery processes, availability, and the different applications must be carefully planned and commissioned.
Reserve Bank of India has directed to store at least seven years of transactional and financial data. Security is the most crucial element in the network. All applications have been built with a conscious approach towards security. The security policies are tightly integrated and regularly scrutinized to leave no room for compromise. All the applications and Operating Systems are hardened periodically for safety.
Essay # 4. The Big Two Architectures of Online Trading in India:
NSE and BSE, the big two exchanges continuously update and upgrade their technology systems to keep delivering according to commitments and promises made to its members, partners, and customers.
It’s difficult to deploy out-of-the-box applications at exchanges as each has a unique architecture based on factors like operations flow, trading volumes, number of members, number of users, and number of locations. The applications like trading, clearing, risk-management, surveillance, index computation, listing, membership, and accounts were developed either in-house or by external software developers.
i. NSE Architecture-NEAT:
NSE has deployed NIBIS (NSE’s Internet Based Information System) for real-time dissemination of trading information over the Internet and NEAT a client-server-based application to help its operations. NEAT stores all trading information in an in-memory database at the server end to achieve minimum response time and maximum system availability for users. The trading server software runs on a fault-tolerant STRATUS mainframe and the client software runs on Windows PCs.
The telecommunications network uses the X.25 protocol and is the backbone of the automated trading system. Each trading member trades on the NSE with other members through a PC located in the trading member’s office. The trading members on the Wholesale Debt Market (WDM) segment are linked to the central computer at the NSE through dedicated 64 Kbps leased lines and VSAT terminals.
These leased lines are multiplexed using dedicated 2 MB optical-fiber links. The WDM participants connect to the trading system through dial-up links. The exchange uses RISC-based Unix servers from Digital and HP for back-office processing. Applications like Oracle 7 and SQL/Oracle Forms 4.5 front ends are used for the exchange functions.
Backup and Recovery:
This has emerged as one of the vital aspects of business continuity. When online exchanges were designed a few years ago, perhaps a lot of emphasis was not placed on this aspect, as it is today. However it’s not difficult to add business continuity processes to an existing network.
As a backup to NSE’s VSAT network, a terrestrial-based trading network was deployed in the middle of 2000. NSE has more than 850 leased lines connected to its nationwide locations. It is the only stock exchange in the country to have a fully-redundant business continuity site in Chennai. NSE has achieved uptime greater than 99.9%, mostly due to internally formulated procedures and continuous review of SLAs with hardware vendors.
ii. BSE Architecture—BOLT:
BSE has deployed an On-Line Trading system (BOLT) on March 14, 1995. It works on a Tandem S74016 platform running on 16 CPUs. The Tandem Himalaya S74016 machines act as the backend to more than 8000 Trader Workstations networked on Ethernet, VSAT and Managed Leased Data Network (MLDN). The systems claim to handle up to two million trades a day.
BOLT has a two-tier architecture. The trader workstations are connected directly to the backend server which acts as a communication server and a Central Trading Engine (CTE). Other services like information dissemination, index computation, and position monitoring are also provided by the system. A transaction monitoring facility in the Tandem architecture helps keep data integrity through non-stop Structured Query Language (SQL).
With the help of Mahanagar Telephone Nigam Limited (MTNL), BSE has setup a MLDN Network comprising 300, 2 Mbps lines and 1500, 64 Kbps lines which connect all regional stock exchanges and offices in Mumbai. Access to market related information through the trader workstations is essential for the market participants to act on real-time basis and take instantaneous decisions.
BOLT has been interfaced with various information vendors like Bloomberg, Bridge, and Reuters. Market information is fed to news agencies in real time. The exchange plans to enhance the capabilities further to have an integrated two-way information flow.
Essay # 5. Online Trading Process:
Online trading is the investment activity that takes place over the Internet without the physical inclusion of the broker. An end user (investor) has to register with an online trading portal like IClCIdirect(dot)com, motilaloswal(dot)com, sharekhan(dot)com, etc. The investor thus gets into an agreement with the firm to trade in different securities according to the terms and conditions listed down on the agreement.
Since the servers of the online trading portal are connected all the time to the stock exchanges and designated banks, order processing is done in real time. Investors can also get updates on the trading and check the status of their orders either through e-mail or through the interface.
A very important aspect is the systems should be able to interface directly with that of the online exchanges without incompatibility issues. The information transmitted across the Internet is safe and cannot be accessed by a third party.
Users are usually given options to link their bank accounts, Demat accounts, and brokerage accounts into a single interface. The “three-in-one” accounts offered by private sector banks, that link up your online trading account to savings banks and demat accounts for easy transaction, have captured the lion’s share of online trading customers. There is also a single window for all exchanges and a single screen for the complete order routing mechanism.
The hardware used comprises Web and application servers, switches, routers, firewalls and security devices, and specialized appliances. The online portals also have off-line storage which is backed up periodically at separate locations. Most portals charge a small registration fee and brokerage based on various conditions. These portals keep focused on customer-centric services and delivery models to attract and retain the attention of their customers.
Essay # 6. Impact of Online Trading on Securities Market:
The prevalence of on-line trading had significant impacts on the trading patterns of investors, trading volume, transaction costs, securities service industry, and overall market operations.
Investor in Control of His Investments:
Now-a-days more investors are logging on to the Internet to put through their stock market trades. The ‘democracy’ of online trading is the key reason why retail investors prefer to transact over the Internet, rather than place orders through their broker.
“Online trading treats all investors equally, whether large or small-sized. It is a democratic medium. It gives the retail customer ready access to the market. The investor is in complete control of his investments and gets the benefits of transacting in real time.”
The number of investors registered for online stock trading has risen three-fold, to 13 lakh, over the past two years. Online trades now account for about 12 percent of the daily turnover on the NSE, up from about 4 percent in 2004, according to brokerage industry estimates.
Emergence of Day Trading:
A new type of trading has emerged what is called “day trading.” It is not really investing at all, but rather making money from minute fluctuations in the price of a stock. A typical person with an on-line account may only make twenty-five transactions a year, but a day trader can make between fifty and two hundred transactions a day.
They are known as day traders because they never hold on to a stock overnight. Day trading is possible only because of the Internet and, more specifically, the faster connections available today. By keeping track of stock prices continuously with fast connections, day traders spot small differences in buying and selling prices of the same stock and take advantage of them.
Again, it is very easy to lose a lot of money quickly with day trading. The estimates of the number of day traders around the country range from 2,000 to 20,000 at any one time, but they account for about 25% of all on-line trades. They add significantly to the problems like slowdowns during heavy periods because that is when they are more active.
Lowering of Transaction Costs:
The transaction costs have been significantly lowered after on-line trading was introduced. Initially, a 0.5 percent of brokerage commissions were applied to both on-line and traditional transactions. Due to the price competition, brokerage commissions for on-line trading continued to be lowered.
Currently, the brokerage commissions for on-line trading are less than 0.1 percent, whereas those for traditional transactions are around 0.5 percent. Lowering of the capital requirements for the establishment of broking-only securities firms prompted appearance of several broking-only securities firms, which are exclusively engaged in on-line trading businesses.
The low fee strategies of these securities firms further accelerated price competition. The speed and lower transaction costs of on-line trading encourage investors to trade frequently in pursuit of short swing profits, making day trading prevalent on the market.
Access to Information:
After on-line trading was introduced, individual investors could have an easy and speedy access to market information. The number of securities market-related websites increased rapidly, providing a variety of information, including quotation information, corporate disclosure, financial information, research papers and financial news, on a real-time basis. Thus, on-line trading contributed to the alleviation of the information asymmetry among the market participants, particularly between the individual and institutional investors.
Essay # 7. Problems Relating to Online Trading:
The top three problems related to online trading were that orders were processed slowly or not at all, that accessing accounts was difficult, and that errors were made in order processing.
These are the more technical problems with trading over the Internet that can lead to the loss of a great deal of money, but there are also problems due to misled or misinformed people. Some of these problems are not even deliberate but stem from the nature of the Internet itself.
Because it is so easy to jump on the Internet, and because it is convenient, on-line trading is easily brought to the average person. Brokerage firms love this because it will bring in a larger consumer base, but many of these new people probably do not have the experience to trade in the stock market. Web sites can be very flashy. Since trading is easy, people associate that with making money easily.
Day trading may sound easy, but it is actually very hard. A day trader is typically very good with computers and has had experience in the stock market previously. They also usually have a good amount of money to start with. About one third of day-traders make money, another third break even, and the other third lose money. Probably only one in ten can actually support a family from day-trading.
Unfortunately, some day-trading companies have made it sound much better than that in their advertising and promotions. Since day trading does not involve making much more than that on each transaction, most of the profit goes to the firm.
The prevalence of on-line-trading resulted in other undesirable consequences too. For example, exploiting the quotation information made public, some devious investors has repeatedly attempted to mislead other investors by placing unreasonably large orders at prices that would be unlikely to be executed. Excessive day trading increased the price volatility too.
Essay # 8. Growth of Online Trading in India:
There is change in the profile of investors registering for online trading. While young Net-savvy retail investors were the first to embrace e-broking, quite a few high net worth individuals (HNI) are now moving to the Internet. HNI investors seem to like the privacy that online trading offers.
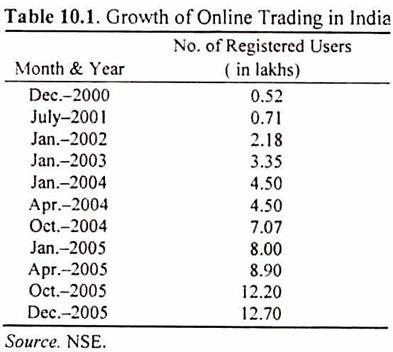
For those who prefer a personal interface with their broker, brokerages are offering exclusive personalized research calls to nudge them on to the online platform. They even provide some of their online customers with a personal investment advisor. The growth of online trading in our country is given in Table 10.1.
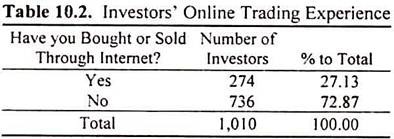
In this background the investors were enquired about their trading through internet.
To the question whether they have bought or sold shares online? Nearly 73 percent of the investors said ‘no’. More than one fourth of the investors said ‘Yes’. This shows that even though the numbers of registered-online investors are increasing a very large number of investors are still away from online trading. This may be due to their inadequate knowledge of the nuances of online trading or due to the lack of infrastructure required for this.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, online trading can flourish when certain conditions are in place and interact with each other positively. Among others, large Internet-using population, well-established communication infrastructure, the provision of incentives for online trading, deregulation and favorable market conditions are necessary to encourage online trading.
The number of investors registered for online stock trading has risen three-fold over the past two years. However, nearly 73 percent of the sample investors have not done online internet trading so far. This shows that investors are yet to learn about the developments taking place in the market place. It should be kept in mind that online trading has both positive and negative effects on the securities market. It is necessary to address the negative effects. Ignoring the risks involved, one might be drowned while sailing the ocean.