In this essay we will discuss about ‘Sales Promotion’. Find paragraphs, long and short essays on ‘Sales Promotion’ especially written for school and college students.
Essay on Sales Promotion
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Definition of Sales Promotion
- Essay on the Objectives of Sales Promotion
- Essay on the Methods of Sales Promotion
- Essay on the Role of ‘Promotion’ in Marketing
Essay # 1. Definition of Sales Promotion:
Sales promotion work is conceived of in two different senses. In a narrow sense, sales promotion work means such activities as are necessary for aiding personal selling and advertising. In a broad sense, sales promotion work includes all those activities which are directed towards promoting or bolstering sales.
From this standpoint, sales promotion work encompasses activities like personal selling, advertising, and innovations in products, pricing or in marketing methods in addition to some auxiliary efforts to personal and impersonal salesmanship.
Promotion is a marketing tool and used both for commercial as well as non-commercial purposes. Promotion is a type of communication from the producer/manufacturer/wholesaler and all those who are in possession of products and/or services and have an intention to part away with the some at a given consideration.
Sales needs stimulation from time to time and persuasive communication to the existing and potential customers is the best way to stimulate and promote sales in any marketing effort. Herein lies the concept of sales promotion.
That is why; Philip Kotler defines sales promotion as an activity which encompasses all the tools in the marketing mix whose major role is persuasive communication.
According to American Marketing Association, sales promotion consists of “those marketing activities other than personal selling, advertising and publicity that stimulate consumer purchasing and dealer effectiveness such as displays, shows and expositions, demonstrations at various non-current selling efforts not in the ordinary routine”.
Essay # 2. Objectives of Sales Promotion:
From the above discussions and definition, we can deduce that sales promotion aims at:
(i) Stimulating the consumers’ decision in favour of the products and services offered;
(ii) Stimulating the dealers’ actions in favour of the products and services dealt in by them with a view to attracting consumers towards the offers so made by them; and
(iii) Maintaining continuous efforts to convince the consumers in such manner and depth that they start purchasing the product of a given quality at a given price and remain with the firm today, tomorrow and day after.
To be specific and precise, the objectives of sales promotion are:
1. To create a brand-image of the product and/or services by way of regular information to the customers regarding the quality, uses, different applications of the product, etc.
2. To educate the consumers in such manner that they are convinced about the usefulness of the products and thereby inclined to take a decision in favour of the product.
3. To let the consumers know of what they want and of the devices with the aid of which they can satisfy their wants.
4. To assist the own sales personnel and to induce the middlemen like wholesalers and retailers so that they can reach the consumers without difficulty and with a minimum of effort.
5. To remove the dissatisfaction of the consumers by adopting a policy or a strategy which would keep the good points of the product in their mind and reinforce a feeling among than that they are getting better deal.
6. To bridge the gap between advertising and personal selling, the two methods of promotion, so that the consumers remain in touch with the product and continue to use or consume the same.
7. To increase the sales of the product by changing the elasticity of demand through various promotional techniques like free gifts, cash discounts, samples, credit facilities, etc.
Essay # 3. Methods of Sales Promotion:
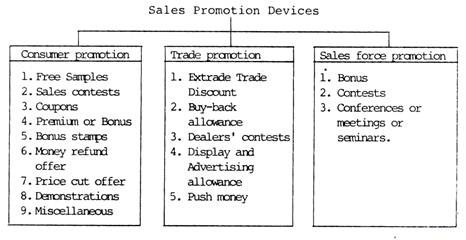
The various methods or devices or programmes that can be used for sales promotion may be shown in the following chart and divided into three basic categories or groups.
These are discussed below in brief:
A. Consumer Promotion:
Sales promotion programmes or efforts directed towards the consumers are done with a view to:
(i) Increasing the consumers’ knowledge about the uses, price, and want-satisfying qualities of the products;
(ii) Attracting the new consumers; and
(iii) Meeting the competitor’s promotional activities.
A firm, in view of the above, attempts to reach the consumers through a place of business or retail shops with the help of the following media of efforts:
(i) Free Samples:
For the introduction of new products in the market, free samples are distributed to the selected customers particularly in the case of cosmetics, perfumes and like products. This system is confined to those products of small value which have off-repeated sales.
To economies the costs, sample packets of smaller sizes are made out by many firms. This system is an effective device of sales promotion as the consumers are provided with an opportunity to examine the product and to see its merits before purchase. Usually, an explanatory literature is added detailing the mode of use and the features of the product.
(ii) Sales Contests:
Contests for consumers are held on the subject of writing a statement. Such statements center round the questions as to the likings of a customer for the product, suggestions in respect of new uses for a product, or formulation of new advertising idea for the product. Such contests give an opportunity to the consumer to win prizes, free travel trip or articles. This is an indirect method of introducing a new product.
(iii) Coupons:
A coupon is small-sized document entitling a consumer to a specified saving on the purchase of a specified product. These coupons are usually issued by the manufacturers through the retailers. The retailers get reimbursement of the value of coupons from the manufacturers. This scheme is useful to attract new customers or to introduce a new article at a concessional rate.
(iv) Premium or Bonus:
On the purchase of some specific product, the premium is given to the buyer by way of either supplying a gift article or providing the opportunity to purchase an article at a greatly reduced price.
According to the mode of offering premiums, the premium scheme falls into two categories:
(1) Premium articles, and
(2) Premium coupons.
In the case of premium article, the gift article is enclosed in the package of products in question and is available at the point of purchase. But the success of the premium article depends upon the wise selection of both gift articles and the specific product that earns premium.
Gift article should be one of good taste and it must be looked upon as the proud possession on the part of buyers because of non-availability of such articles in the market.
As regards the product earning premiums, it must be of small size, of common use as well as short lasting in character. The premium coupons attract rewards in various ways. Certain minimum number of coupons may be exchanged for sane enumerated gifts, for obtaining other products at concessional rates or for cash amounts.
(v) Bonus Stamps:
The consumers are given bonus stamps in proportion to their purchase values. They collect these stamps and stock for a sufficient quantity to obtain the desired merchandise in exchange of the stamps.
(vi) Money Refund Offer:
This scheme is usually mentioned in the advertisement itself to the effect that the manufacturer will return the price within a stipulated period- if the consumer is not satisfied with the product. The product ‘Bull-worker exerciser’ was promoted this way.
(vii) Price-Cut Offer:
This is a kind of price reduction for a temporary period. The consumers are offered a certain amount of money off from the regular price of the product for a specific period only. This is adopted to attract the customers from other brands.
(viii) Demonstrations:
These are arranged with the help of technical experts or sales demonstrators either at a centrally located place or at fairs and exhibitions during festive seasons to promote and popularise the new and existing products. They provide ample opportunities to the manufacturers, both large and small, for explaining the special features and usefulness, and hence for extending the sales horizon of the business.
In addition to sales promotion and buyers’ education in the use of products, these demonstrations can give significant ideas to the industrialists for innovating their products or services to the benefit of all concerned in any business.
(ix) Miscellaneous:
Various other methods, such as counter display cards, prizes, gift cards, etc. are also made use of to induce the consumers to buy the product.
B. Trade Promotion:
The trade promotions refer to the sates promotional programmes or efforts through the middlemen like wholesalers or retailers or dealers or all. These are undertaken with a view to inducing the middlemen to keep large stock of the products and increase the sales volume thereby.
The following auxiliary efforts fall within this group:
(i) Extra Trade Discount:
This involves an offer of higher rate of trade discount to the dealers with a view to inducing them to buy and resale the manufacturer’s product to the ultimate consumers. Such extra or higher rate of discount is given usually on a minimum value of purchase during a defined period of time.
(ii) Buy-Back Allowance:
Under this scheme of sales promotion, a certain amount of money is offered by the manufacturer to the dealer for additional trade based on the quantum of purchases made on the first trade deal.
(iii) Dealers’ Contests:
The contests for dealers are intended for inducing them to devote greater efforts or for obtaining new sales idea in the task of sales promotion. Prizes are given to the best group of dealers or marketers on the basis of their sales performances.
The success of consumers requires the enlistment of a sufficiently large number of participants, competent judging of entries and absolute fairness to all contestants in declaring results. The rewards are given in cash or in merchandise.
(iv) Display and Advertising Allowance:
This allowance is given to a dealer by a manufacturer on the basis of space provided by such dealer to display the manufacturer’s product in the shop.
(v) Dealer-Listed Promotion:
This method involves the incorporation of the names and addresses of the dealers on the advertisements and publicity materials like diaries and calendars, etc. The two-fold functions of consumer education and convincing of dealers are achieved in this effort.
(vi) Push Money:
This is a kind of incentive payment in cash or in kind to the dealers for sales promotion of products and is generally determined at a fixed rate per product sold.
C. Sales Force Promotion:
Personal selling or salesmanship is by far the best method of sales promotion. So, the sales persons employed by a firm should be adequately rewarded.
In these respects, a firm adopts the following types of programmes:
(i) Bonus:
The firm fixes a quota of sale per sales person per period of time and also a rate of bonus to be paid when the actual sales exceed the quota. This induces the sales person to augment the sales.
(ii) Sales Faroe Contests:
Same as dealers’ contests.
(iii) Sales Conferences:
These are organised by the manufacturers to educate the sales force for new products and novel selling techniques.
Essay # 4. Role of ‘Promotion’ in Marketing:
Promotion plays a very important role in marketing. The term ‘promotion’ in the field of marketing, refers to a function which is directed towards persuading the existing and potential customers to go in for a given product or service.
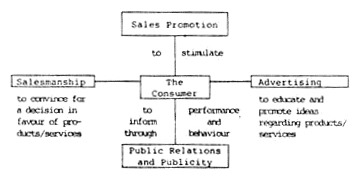
It is persuasion, communication and information—all combined in a judicious manner – the direct result of which is the customers’ inducement either to continue or to start reposing confidence in or to switching over to the firm’s product of a given quality at a given price. ‘Promotion’ is a broad term which is conceived of as a ‘marketing communication mix’ by Philip Kotler.
According to Philip Kotler, ‘promotion’ consists of, and combines in it, the functional elements of:
(i) Sales promotion,
(ii) Advertising,
(iii) Salesmanship, and
(iv) Public relations and publicity.
This is represented below in a schematic diagram:
The basic role of ‘promotion’ in marketing is that it is a powerful tool for increasing sales and combating competition when properly planned. Promotion is something extra which either precedes or follows the actual selling.
It is an action-packed and strategy-oriented programme which establishes and reinforces the feeling among all who are concerned with the selling and also among the consumers that they are being dealt with appropriately and being taken in a right stride. It is a direct as well as indirect inducement which strikes when the iron is hot and thus a favourable decision comes forth.