In this essay we will discuss about ‘Scientific Management’. Find paragraphs, long and short essays on ‘Scientific Management’ especially written for college students.
Essay on Scientific Management
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Definition of Scientific Management
- Essay on the Characteristics of Scientific Management
- Essay on the Objectives of Scientific Management
- Essay on the Principles of Scientific Management
- Essay on the Implications of Scientific Management
Essay # 1. Definition of Scientific Management:
Scientific management refers to a school of thought that was based on the notion that the scientific method could be applied to the work place and the related managerial activities. (The major contributors were F.W. Taylor, Gilbreth and H.L. Gantt.) These managers attempted to apply scientific and rational principles for handling men, machines, materials and money.
This challenge took two major forms:
1. Identifying how to increase productivity (output/input) by making the work easier to perform; and
2. Determining how to motivate the workers to take advantage of these methods and techniques.
Thus, the principle of scientific management may be defined as “the use of thorough investigation, controlled experimentation, and careful interpretation of the relevant data that provides a reliable basis for the determination and evaluation of new facts to be used by managers.”
Essay # 2. Characteristics of Scientific Management:
The following are the characteristics of scientific management:
1. Production planning.
2. Analysis and scientific use of different production techniques.
3. Examination of skill, efficiency, abilities and aptitude of the labour.
4. Analysis of plants to be used in production, time involved and cost of installation. A thorough investigation of the productivity of both labour and capital, including plant.
5. Attempt to increase production.
6. Attempt to reduce the cost of production.
7. Provision for proper wage policy based on incentives to workers.
8. Attempt for harmony and co-operation between the management and the workers.
9. Better planning.
10. Effective co-ordination; and
11. Effective control.
Essay # 3. Objectives of Scientific Management:
The following are the objectives of Scientific Management:
1. To make provision for the use of knowledge and skill of production.
2. To standardise the plants, tools, materials and working conditions so as to raise the level of production.
3. To revolutionize the whole process of production and marketing including purchase, sale, production procedure, plant and machinery, accounting, materials management etc.
4. To reduce the possibility of slackness in production, accidents etc.
5. To help in proper guidance and leadership, regular and adequate direction on proper lines, timely communication, better co-ordination, mutual respect, good human relations and fruitful co-operation.
6. To conduct surveys and organise researches so as to mate the management a living and result-yielding science.
7. To help the labour in overcoming his difficulties and solve their organisational as well as domestic problems in a manner in which he feels satisfied and prepares himself for hard and selfless but rewarding work.
8. To help all-round mental, physical and technical development of the workers.
9. To help increase the levels of wage, profit and consumers service of the highest degree.
10. To effect new and scientific technique in production.
11. To serve the enterprise, the economy, the nation and the society in a manner in which the society expects.
Essay # 4. Principles of Scientific Management (Taylor):
The four basic principles of scientific management by Taylor are as follows:
1. Develop a sciences for each elements of person’s work, which replace the old rule of thumb method.
2. Scientifically select and then train, teach and develop the worker, whereas in the past he chose his own work and trained himself as best as he could.
3. Heartily co- operates with the workers so as to ensure that all of the work is being done in according with the principles of science which has been developed.
4. There is an almost equal division of the management of the works and the responsibilities between the management and over all works for which they are better fitted than the workers, while in the past almost all of the responsibility were thrown upon the workers.
Essay # 5. Implications of Scientific Management:
1. To determine the best method for performing each task.
2. A workers when selected on a scientific basis could be given responsibility for the task for which suited.
3. Scientific education and development of the workers is necessary.
4. Intimate and friendly co- operations between the management and their workers is essential.
Taylor differentiated the above four principles from the mechanism of management such as tine study, standardisation of tools, time-saving devices and so on.
His comprehensive scientific management system is characterised by five important features:
1. Organisational and technical improvements such as better machine operations, cost and management accounting, purchasing and stock and tool rooms control.
2. A planning department that was responsible for coordinating the overall operation and assigning jobs.
3. The use of functional foreman who was responsible for a single functional activity within the manufacturing process.
4. Time study to determine the rate at which a job should be done.
5. An incentive wage system.
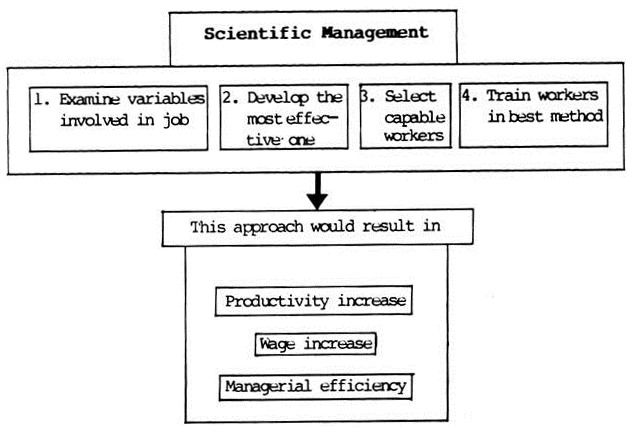
Schematically, Taylor’s principles are:
Regarding scientific approach to management, Taylor himself summed up his combination of principles in the following terms:
1. Science, not rule of thumb,
2. Harmony, not discard,
3. Co-operation, not individualism,
4. Maximum output in place of restricted output,
5. The development of each man to his greatest efficiency.