After reading this article you will learn about Finance Functions of Business:- 1. Meaning of Finance Function 2. Objectives of Finance Function.
Meaning of Finance Function:
“Finance is that administrative area or set of administrative functions in an organisation which relate with the arrangement of cash and credit, so that the organisation may have the means to carry out its objectives as satisfactorily as possible.”
It has been said that a businessman takes money to make money. This is not true. The statement needs correction. If you have money, and you manage it properly, you will make more money. This means management of finance is necessary for all.
Objectives of Finance Function:
Funds are obtained for investment in business. These funds must be duly protected and conserved. We must make maximum use of these funds. There are twin objectives, namely, profitability and liquidity of funds. These are conflicting and finance executives must secure the balance and optimize the utilisation of funds.
The major objectives of finance function or financial management are:
1. Procurement of money needed by business;
2. Keeping and increasing the invested money through sound financial policies and programme; and
3. Generating income or profit for the business.
Business finance usually involves the following vital functions:
1. Financial planning, forecasting of cash receipts and disbursements — cash flow statement;
2. Raising of funds, either equity capital or fixed interest capital which includes both preference share capital and loan capital (securing of funds);
3. Use and allocation of funds (administration of funds); and
4. Financial controls (budgets and other controls).
Please note that wise and integrated approach in financial management alone can accomplish both productivity (maximum wealth) and satisfaction.
Comments:
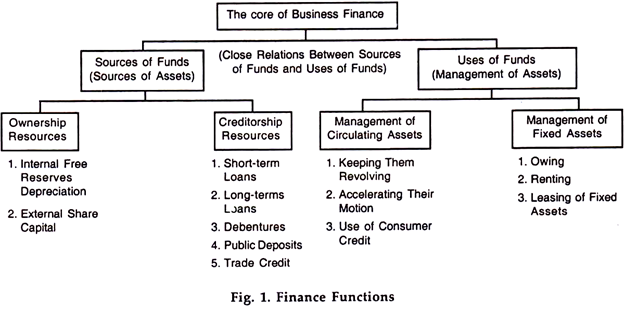
1. Problems of raising capital funds and problems of managing assets are the two sides of the same coin.
2. While raising additional capital from different sources there are seven aspects demanding careful consideration:
(i) Cost of raising capital;
(ii) Compulsory periodical cash payment for the use of capital;
(iii) Period for the use of capital;
(iv) Control to be sacrificed;
(v) Restrictions on managerial freedom;
(vi) Collateral security-pledge/ mortgages; and
(vii) Convenience in securing funds.