This article throws light upon the twelve main factors affecting the layout of an industrial building. The factors are: 1. Organisation of Departments 2. Location of Production Departments in the Building 3. Position of Service Departments 4. Premises 5. Size and Local Conditions of Site 6. Type of Construction 7. Ventilation and Air Conditioning 8. Appearance 9. Plant Protection and Few Others.
Factor # 1. Organisation of Departments:
It means, where various production departments such as machine shop, welding shop, assembly shop etc. should be located in the building? What should be their size etc.?
For this purpose the processes or operations are studied and product analysis should be made.
This will show:
(i) What is to be produced?
(ii) How much is to be produced?
(iii) What will be the sequence of operations?
(iv) How much time each operation will take?
(v) How the machines can be best grouped?
(vi) What will be the capacity of machines and their production etc.?
(vii) The amount of space needed and necessity of special provisions, if any.
Factor # 2. Location of Production Departments in the Building:
The various production departments should be located in such a way so that the traffic or movement of workers should be easy. Flow of materials within the department and also between one department should be economically and neatly managed.
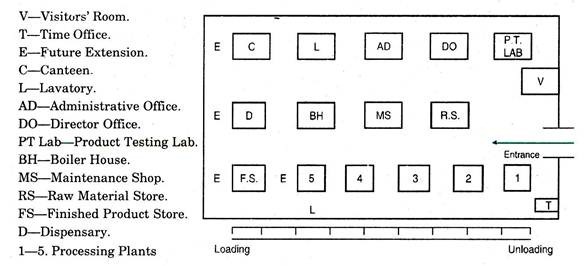
In the diagram given below “Layout of a Chemical Factory” is shown. Material flows from Raw-material Stores (R.S) to production plants (1 to 5), then after processing it reaches Finished Store (F.S.). The layout shows that it shortens the travel of materials and movement of persons. Loading and unloading is done nearby. Such a layout of industrial building is proved to be most economical.
Factor # 3. Position of Service Departments:
Service departments mean canteen, stores, toilet rooms, first-aid, water, schooling, conveyance etc. These should be properly positioned after making the plant layout. After planning the plant layout, remaining space should be suitably allotted for all these services. These should be located in the light of factory as well as workers’ interest. For this, Factory Act must be followed.
Factor # 4. Premises:
The various sections of departments of the factory can be arranged into three main group’s i.e., Administrative, Service and Production departments.
As far as possible administrative department should be located in a separate wing, where there should be no noise and disturbances due to movement and vibrations of machines etc.
General Service departments such as finished parts store, tool rooms, and toilet should be as central as possible. Safety provisions for the employees should be as central as possible. Raw material stores and heavy machinery stores should be near the production department.
The various shops of production departments such as foundry, welding, machine shop, smithy shop etc. should be properly arranged.
Factor # 5. Size and Local Conditions of Site:
If the site is of small size and the manufacturing methods involve the gravity flow of products e.g., chemicals and paints, a multi-storey building must be designed. In this case the flow of material will be much easier.
When heavy machinery is used and bulky work tackled e.g., locomotives or aircraft etc., a single-storey building is preferred.
Usually single-storey building preferred, if land is cheap. It involves lighter foundations, less vibrations, better supervision, flexibility with regard to layout, more effective floor area, better natural lighting and no necessity of lifts and elevators etc.
Factor # 6. Type of Construction:
The chief points concerning, structural material are as below:
(a) Strength,
(b) Durability,
(c) Safety,
(d) Speed of Construction, and
(e) Cost.
The industrial building may be made of timber, bricks, steel frame or concrete.
Today timber is rarely used because of the danger of the fire and high insurance rates. The brick construction is very common for walls, office building.
Now-a-days steel frames such as steel girders, columns, roof trusses etc. are commonly used because of long life and low insurance rate. Today, because of low capital investment and less depreciation of building, concrete or pre-cast constructions are used.
When light structures are needed galvanized iron sheet roofs may be used. Actually, the choice of the type of construction will depend upon the availability of materials and the specific requirements of the plant.
Factor # 7. Ventilation and Air Conditioning:
This factor is of extreme importance. As heat, dust, moisture, fumes, smoke etc., are greatly produced in manufacturing processes, these reduce the percentage of oxygen and increase the percentage of carbon dioxide in the factory environment, which makes breathing difficult and develop certain diseases.
Hence proper ventilation and air conditioning is very essential. These are conducive to health and efficiency and will create lively and healthy atmosphere in the factory.
Great care was taken in past that clerks on small salaries were comfortably housed and they would not have been expected to do good work unless so cared for, but high priced machines were only too often expected to produce good results in spite of all sorts of physical discomfort and inconvenience to workers.
There is no difference between the psychology of the office and that of shop. Workmen can naturally produce more and better in well-ventilated and air conditioned rooms.
For comfortable environment, an employee requires 0.03 cu.m of fresh air per minute at a temperature of about 27°C. In this respect, the Factories Act has made some provisions and those must be followed while making the layout of the building.
Air conditioning is required to be done for controlling the air temperature, humidity, cleanliness and distribution of air. Temperature is controlled by heating the air in winter and cooling it in summer. Humidity is controlled by adding moisture in the air during winter, and by removing it in moist summer.
Cleaning is done by removing foreign materials such as dust etc., from air by:
(a) Forcing the air to pass through spray of water,
(b) Passing air through filters, and
(c) Using electronic precipitators.
Factor # 8. Appearance:
A huge capital is invested on the purchase of machinery, building construction and other equipment’s. The appearance of the factory also plays important role in raising productive efficiency and reduces labour turnover. Therefore, this factor should not be neglected. With a small additional expense, it can be made beautiful.
The windows, doors and colouring scheme should be properly planned. Just as a well-designed machine is pleasing to look at, so a well-designed factory building must be pleasing to look. Therefore, it should be kept and coloured in such a way that the atmosphere created is bright, cheerful and restful.
Factor # 9. Plant Protection:
The factory should be surrounded by boundary wall all around and boundary walls must be covered with broken glass pieces or fencing wire should be laid over it.
To prevent theft, strict security guards should be employed. There should be only one main gate and it should always be kept under the control of safety guard. Unauthorized persons should not be permitted to enter inside without permission and photography should be strictly prohibited.
Provisions for storing inflammable materials should be made far away from the main building. For this, Factories Act must be followed.
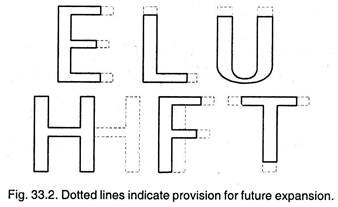
Factor # 10. Provisions for Future Expansion:
Enough space in shops must be allowed for future expansion. The usual practice to layout buildings corresponding to shapes of such letters as U, H, E, T, L, and F shown in the figure depending upon departmental problems and flow of materials through the plant is adopted. All the plans shown in the figure, lend themselves to expand in several directions from end walls. Dotted lines show space for future expansion.
Factor # 11. Sanitary Convenience:
Provisions for good lavatories, washing and dressing facilities must be made in the layout at different central places. Care should be taken to keep the equipment as simple as possible and of a quality consistent with the workers’ social status. This will inspire health and efficient atmosphere.
All the above factors must be taken into account while planning a general factory layout. Various departmental heads should sit and consult together and an attempt be made to arrange a best possible layout, which may produce maximum efficiency with minimum expense.
Factor # 12. Lighting:
Good lighting provides safe working place and helps in increasing vision. This increases the efficiency of workers and also reduces accidents.
While installation of light points, the factors given below should be considered:
(i) The light should be cool or given off less heat.
(ii) There should be sufficient visibility of the complete job.
(iii) There should not be any glare.
(iv) Shadows should be avoided.
(v) Brightness must be uniform throughout the area.
(vi) Light must not be dazzling.
The amount of light required for any job will depend on the nature and type of job. For precision job even hundred lumens/m2 of light may be used.
Role of Illumination on Productivity:
(i) When an industry is properly illuminated we can utilise these resources in better way e.g., proper illumination reduces accidents frequency and reduction in accident means reduction in wastage of time, labour, money (for repairing damage of machines and plant, compensation etc.) and men.
(ii) Proper illumination also leads to reduction in errors and hence reduction in spoilage of work. Thus, time put on the manufacture of such spoiled works and expenditure incurred on raw material, labour and power on the spoiled work can be saved.
(iii) Good lighting helps in maintaining health of the worker by saving him from eye strain and headache, thus the man time can be utilised in better way which would, otherwise, have been lost due to his illness.
(iv) Adequate illumination provides comfortable conditions of work, which increases the speed of work, leading to increase in productivity.
(v) Industrial psychology has proved that good lighting and air movement helps in improving human relations. Because dim illumination produces disappointment and uncomfortable conditions to workers which leads to bad health, and mental friction and thus wrong mental attitude, spoiling the employer-employee relations.
Thus, it is clear that by providing good lighting, productivity (output per man-hour) increases and at the same time wastage is reduced, thereby reducing the cost per unit of output.
Reduced cost of production will result in the fall of prices, and reduction in prices will mean rise in demand and thus improvement in the standard of living and this will create and develop new markets for the commodity. It will encourage the producers to extend their factory and set up new units, which will help in the employment of other workers.
More production at the lesser cost will give more benefit to the owner from which he can increase the wages of workers and can provide better working conditions to them. Thus increased productivity has so many advantages to the owners, the workers and the community as a whole.