After reading this article you will learn about:- 1. Meaning of Freight Forwarders 2. Freight Forwarders 3. Types of Forwarders 4. Freight Forwarders and Customhouse Brokers.
Meaning of Freight Forwarders:
The physical movement of goods for the export destinations is much more complex as compared to the domestic market. To start with, the usual packing designed to protect and/or promote a product while on display is not suitable when considering the export market.
The packing meant for shipping has to be specific for that purpose if the goods are to be properly protected during shipment, because of greater numbers of hazards involved, the length of time during which the cargo is in transit, and a carrier’s limited liability, the shipper should obtain marine insurance.
In addition the shipper must obtain marine insurance cover to protect him from any adverse situation. In addition to these points the shipper has to take necessary packing precautions to minimize any chance of damage.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The containerization is one of several transportation modes that can achieve the desired goal but again stuffing of the goods into a container also calls for some degree of expertise, which is gained, only through practice and learning.
Besides packing, there is a greater number and volume of shipping documents that must be filled up to satisfy the governmental regulations at the point of exit and at the point of entry at the destination market.
On top of all these activities there is price factor associated with the movement and clearance of the goods. These prices are in no way very small and in the case of export bidding they may mean success or failure with the contract and/or profits.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
To overcome all these painstaking exercises either you have to be proficient in tackling these activities or use outside help. Fortunately there are experts who specialized in the physical movement of the cargo and are called the Freight Forwarders and Customhouse brokers. They belong to the service sector of the industry and are vital for both the importers and exporters.
Freight Forwarders:
They are businessmen who specialize in the international movement of cargo and render expert advice to their clients.
Their activities are summarized as under:
1. Packaging and labeling,
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. Warehousing, and
3. Selection of mode of transport considering the size, weight, characteristics of the goods involved.
4. They assume full responsibility for the documentation, insurance, vessel space booking, and arrangement of collection of goods from seaports, railways, and container yards of the incoming and outgoing cargo right up to the client’s desired destination.
5. They also specialize in Group age system where under they collect at one of their depot numerous small shipments bound for the same destination and consolidate them into single larger consignment. This way they help the small and medium size exporters to get much cheaper/ competitive freight rates. This system is no doubt less expensive but in many cases takes longer time for final delivery.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Generally they work on a very small percentage of the total value of the goods handled; this is called as their handling charges. Their clients are but one source of income, they also collect commission from transport companies and bulk discounts from carriers and bulk warehousing, part of which they divert to clients for winning the customers and/or for cementing the business relationships.
They do not own the transport facilities but will buy from the most appropriate and competitive source. They also act as an agent when they perform functions on behalf of and under the instructions of the principal or the trader or the carrier. As an agent the forwarder may procure the services of third parties who will perform the packing, storage, transport, handling and custom clearance of the goods.
The agent thus acts as an intermediary without taking any title to the net contracts. The concerned principal then enters into direct contractual relationship with the service providers. As with the other agents the forwarders owes the principal various duties including the duty to inform and the duty of diligence.
On the other hand there are cases when the forwarder acts as a principal, he contracts directly with the exporter or importer. The customer will deal only with the forwarder, who will issue a single bill to the customer for the total amount of the services rendered. As principal, the forwarder is generally liable for the errors or breaches of the sub-contractors.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It is also possible for a forwarder to enter into a “hybrid” arrangements, acting as agent for certain functions and as principal for other functions.
Types of Forwarders:
1. Consolidators or Non-Vessel Operating Common Carriers (NVOCC). They assemble diverse smaller shipments, from various customers so as to make up full container loads, thus obtaining lower freight rates. Some consolidators offer regular shipments on seagoing vessels, which they do not own. These are referred as NVOCC’s.
2. MTO or multimodal transport operators. They offer, “one stop shopping” for traders. It enables the traders to completely outsource or sub-contract their export logistics to a single service provider. Multimodal transport operators typically offer “door to door” transport inclusive of all functions falling in between the export and import destinations.
3. Customs Brokers. In this case they act as the agents of the exporters and/or importers in order to process customs declarations and other formalities and they pay duties/taxes. Such Forwarders are bonded by custom houses or banks or insurance companies since they handle large sum of money.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
4. Port Agents. They represent the shippers at the point where the goods are transferred from one transport mode to another.
5. Airfreight Agents. They process shipments through airlines and normally has the authority to issue Air Way Bills. They also handle the related customs formalities.
6. Loading Brokers. They act as the agents of ship owners to obtain and process cargo shipments. Generally a freight forwarder will represent the shipper while loading broker represent the ship owner.
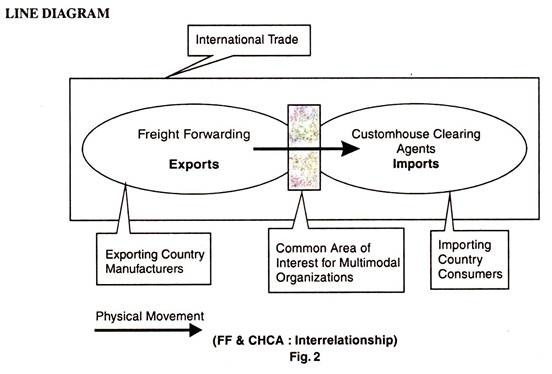
Freight Forwarders and Customhouse Brokers:
The freight forwarders generally work for the export cargo and the customhouse brokers for the import cargo. However their activities has lots of overlapping. As such each one can do the functions of the other or both.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Both of them has following activities as their main tool of business operation:
1. International cargo traffic operations,
2. Govt. export/import rules & regulations (domestic and overseas),
3. Handling extensive volume of international trade related documentation.
4. Custom clearance.
5. Expert packaging advice, and
ADVERTISEMENTS:
6. Negotiation of most effective freight and insurance rates.
The freight forwarders has one important role in the sense that they provide vital price information to exporters/importers for calculation of net price / landed price covering various INCO terms. They are also in possession of strategic trade information on specific cargo that they handle so sometimes they can provide vital inputs for export/import strategic marketing.