This article provides an overview on Product Life Cycle.
The product life cycle concept derives from the fact that a product’s sales volume and sales revenue follow a typical pattern of five-phase cycle. The life cycle is a fact of existence for every product. It is similar to the human life cycle.
The length of the life cycle, the duration of each phase and the shape of the curve vary widely for different products. But in every instance, obsolescence or decay eventually occurs when the need disappears or a better, cheaper and more convenient product may suit the same need or a competitive product due to superior marketing strategy suddenly gains a decisive advantage.
The product life cycle should be preferably termed as product market life cycle as it is related to a given particular market. For example, an old product (in the market of U. S. A.) will have a new life cycle when it is introduced into a foreign market, say, in India.
The product life cycle concept indicates that the product is born or introduced, grows, attains maturity and the point of saturation in that market and then sooner or later it is bound to enter its declining stage e.g., decay in its sales (history).
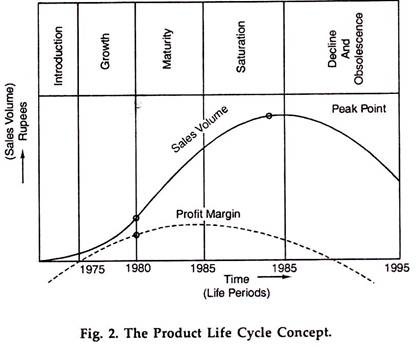
This life cycle of a product is depicted below:
Note: 1. Introduction: Sales are starting. 2. Growth: Rising sales at increasing rate. 3. Maturity: Rising sales at decreasing rate. 4. Saturation: Stable sales. 5. Decline: Falling sales.
Every product moves through a life cycle having five stages: introduction, growth, maturity, saturation, and decline (some authors include saturation into maturity). The life cycle gives the sales revenue and profit margin history of a product over a time frame.
1. Introduction:
In the early stage when the product is introduced in a market, sales revenue begins to grow but the rate of growth is very slow. Profit may not be there as we have low sales volume, large production and distribution costs.
We may require heavy advertising and sales promotion. Products are bought cautiously on a trial “basis. Weaknesses may be revealed and they must be promptly removed. Cost of market development may be considerable. In this stage product development and design are considered critical.
2. Growth:
During the growth stage, the rate of increase of sales turnover is very rapid. Profits also increase at an accelerated rate. In spite, of competition, we may have rising sales and profits.
The firm gives top priority to sales volume and quality maintenance may have secondary preference. For marketing success, manufacturing and distribution efficiency are vital factors. In this stage effective distribution and advertising are considered as key factors.
3. Maturity:
During this stage keen competition brings pressure on prices. Increasing, marketing expenditure and falling prices (in the battle for market share) will reduce profits. Additional expenditure is involved in product modification and improvement or broadening of product line.
Marketers have to adopt measures to stimulate demand and face competition through additional advertising and sales promotion. Overall marketing effectiveness becomes the key factor in the stage of maturity.
4. Saturation:
The saturation point occurs in the market when all potential buyers are using the product and we have only replacement sales. Consumption achieves a constant rate and the marketers have to concentrate exclusively on a fight for market share (with higher marketing expenses). Prices may fall rapidly and profit margins may become small unless the firm makes substantial improvements and realizes cost economies.
5. Decline Stage:
Once the peak or saturation point is reached, product inevitably enters the decline stage. It may be gradually displaced by some new innovation. Sales drop severely, competition dwindles, and even then the product cannot stand in the market.
It may be priced out of the market by other new innovations. At this stage price becomes the primary weapon of competition, and we have to reduce considerably expenditure on advertising and sales promotion. Cost control becomes the key to generate profits.