After reading this article you will learn about buyer’s motive and decision making process for purchasing a product.
Meaning of Buying Motive:
A motive is a drive or an urge for which an individual seeks satisfaction. Thus, any urge moving or prompting a person to purchase decision is called a buying motive. According to S A. Sherlekar. “A buying motive is the reason why a person buyers a particular product. It is driving force behind buying behaviour and may be based on psychological or physiological wants”.
Thus, a motive or purpose of the purchase is mental instinct. It is not imposed or created. It comes from within the man. Some of the buying motives for example are food and drink, comfort to attract opposite sex, welfare of beloved ones, freedom from fear and danger, to be superior, social approval to live longer, cleanliness, efficiency, style and beauty, curiosity etc.
“A motive is the inner state that energizes, activates or moves…and that directs or channels behaviour toward goods.” – Berelson & Stener
ADVERTISEMENTS:
“A motive may be defined as a drive or an urge for which an individual seeks satisfaction. It becomes a buying motive when the individual seeks satisfaction through the purchase of something.” – W.J. Stanton
“A motive is an inner urge that moves or prompts a person to action”. – R.S. Davar
“Buying motives are those influences or considerations which provide the impulse to buy, induce action or determine choice in the purchase of goods or services”. – D.J. Durian
Buyer Decision Making Process:
The most basic and important requirement for the marketer is to understand how consumers make choices. According to Atzen and Fishbein, “human beings are usually quite rational and make systematic use of information available to them. People consider the implications of their actions before they decide to engage or not to engage in a given behaviour”.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
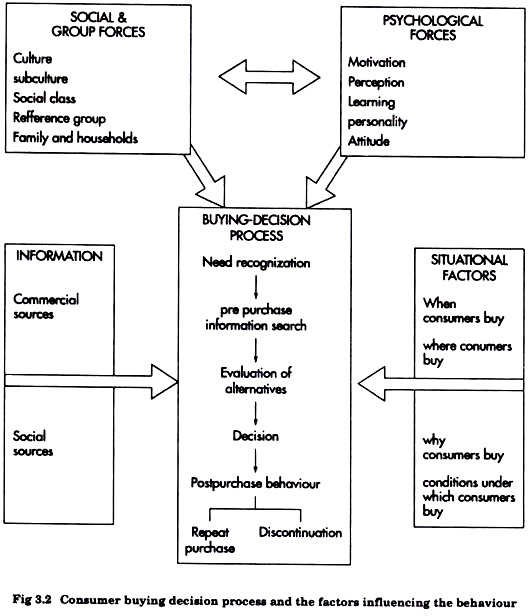
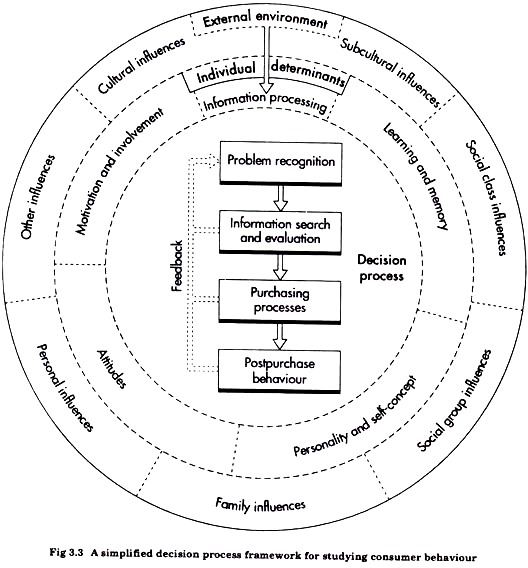
Every buying decision involves an element of active reasoning. Broadly, in making a purchase decision the consumer goes through the following stages (Fig. 3.2):
1. Need recognition
2. Pre purchase information reach
3. Evaluation of alternatives
ADVERTISEMENTS:
4. Purchase decision
5. Post purchase behaviour.
1. Need Recognition:
The buying process starts with need recognition. The person is motivated to act only when he has some unsatisfied need. If some needs are not in activated stage then they can be made activated by providing the information about the product.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
For example, a working woman feel the need for washing machine. The recognition of need will activate her to search for any washing aid and it will result in some decision.
2. Pre Purchase Information Search:
After recognizing the need, the person is involved in gathering the information about the product or service. Search may be of two types: Internal search refers to recalling the relevant information stored in the memory.
External search refers to the deliberate and voluntary seeking of new information regarding the product under consideration. After collecting the information from different sources the person shows the interest in these products.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
3. Evaluation of Alternatives:
Once the interest in the product is aroused, the person makes final decision using certain evaluative criteria like product attribute, the relative importance of each attribute to him, brand image, attitudes towards the different brands etc. The evaluation stage represents the stage of mental trial of the product.
4. Purchase Decision:
After the evaluation, the consumer develops the intention either to purchase or reject the product. The final purchase will however, depend on the strength of positive intention that is the intention to buy.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
5. Post Purchase Behaviour:
After making the purchase decision, the person shows the response of that purchase. It is called as post purchase behaviour. It may be positive or negative. If a consumer is buying something for the first time then from the behavioural view point it may be regarded as a trial.
The trial enables the person to gain learning about the product purchased. If the learning is positive, then it result in repeat purchase and if it is negative then it result in discontinuation.
In case of consumer durable product the person’s learning does not result in repeat purchase or discontinuation because these products are one time purchase products. In these cases the learning is being stored in memory and then it serves as influence for the decision of the reference group members.