The Companies Act recognises the following three types of resolutions: 1. Ordinary Resolution 2. Special Resolution 3. Resolutions Requiring Special Notice.
Type # 1. Ordinary Resolution:
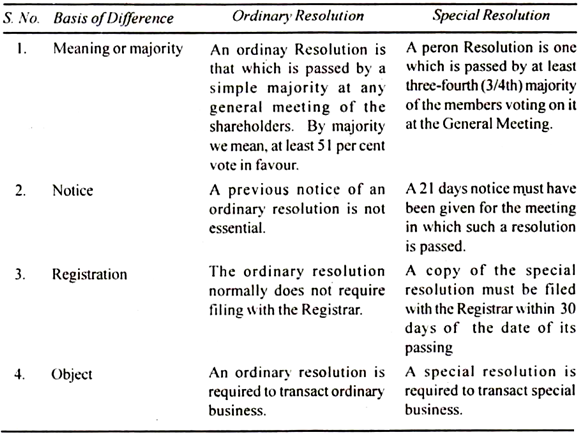
An ordinary resolution is that which is passed by a simple majority at any general meeting of the shareholders. The resolution may be passed by a show of hands or by a poll. A 21 days notice must have been given for the meeting in which such a resolution is passed. Any matters can be decided through an ordinary resolution unless the Companies Act or the Articles of the company provide otherwise.
Objects:
Following are some of the matters which can be decided by an ordinary resolution:
1. Approval of statutory report.
2. Approval of directors report.
3. Approval of final accounts.
4. Declaration of dividend.
5. Appointment of directors.
6. Election of directors.
7. Issue of shares at discount.
8. Appointment of auditors and their remuneration.
9. Alteration of share capital.
10. Change in the rights of shareholders of any class.
11. Creation of reserve fund.
12. Conversion of fully paid-up shares into stock.
13. Sale of the whole or part of the company’s undertaking or business.
Specimen of Ordinary Resolutions:
1. Issue of shares at discount (Sec. 79). “RESOLVED that the Directors of the Company be and are hereby authorised, subject to the sanction of the court, to issue 10,000 shares of Rs. 10 each in the capital of the Company at a discount of not exceeding Rupee one per share.”
2. Increase in the number of directors (Sec. 258). “RESOLVED that (subject to the approval of Central Government) the number of existing directors be increased from……………………….. to…………………… and Mr………….. and Mr…………. be and they are hereby appointed as additional directors.”
3. Removal of director (Sec. 284) “RESOLVED that Mr…………………… Director of the Company regarding whose removal special notice has been received and has been duly heard as required by Section 284(3) of the Companies Act, 1956, be and is hereby removed from his office of director of the company.”
Type # 2. Special Resolution:
A special resolution is one which is passed by at least 3/4th majority of the members voting on it at the General Meeting. A 21 days notice must have been given for the meeting in which such a resolution is passed. Notice calling the meeting should indicate that the resolution is intended to be proposed as a special resolution.
The main feature of special resolution is that the number of votes cast in favour of the resolution should be three times the number of votes against it.
Objects:
The following are some of the matters which can be decided by a special resolution:
(1) Alteration of the name of company.
(2) Alteration of the objects of the company.
(3) Alteration of articles of association.
(4) Change of registered office from one state to another state.
(5) Reduction of share capital.
(6) Creation of reserve capital.
(7) Payment of interest out of capital.
(8) Fixing directors’ remuneration.
(9) Voluntary winding up of a company.
(10) Making the liability of directors unlimited.
(11) Application to the court to wind up the company.
(12) Appointment of inspectors to investigate the affairs of the company.
(13) To bind the company by an arrangement or compromise made.
Specimen of Special Resolution:
1. Alteration of name of the company. RESOLVED that the name of the company be and is hereby altered from…………………. Limited to………………………… Limited and the Central Government be officially informed for the purpose of securing their consent of such alteration.
2. Voluntary winding up of the company. “RESOLVED that the company be wound up voluntarily and that Mr……………………….. of………. be and is hereby appointed liquidator for the purpose and that this be and is hereby passed as a special resolution pursuant to Sec. 484 of the Companies Act, 1956.
3. Alteration of articles of association. “RESOLVED that clause……………………………. of the Articles of Association of the Company be altered by omitting the following words therefore
“………………………….”
and substituting instead of the following words:
“………………………….”
Type # 3. Resolution Requiring Special Notice:
The Indian Companies Act, 1956 has introduced a new type of resolution for the passing of which special notice has to be given. Some matters specified in the Act cannot be moved for discussion at 3 General Meeting unless a special notice is given to the company.
A notice containing the intention to move the resolution had to be given in such cases at least 14 days before convening the meeting in which it is proposed to be moved. The company in turn should give members the notice of that resolution at least seven days before the holding of the meeting. Such resolution may be ordinary or special resolution.
Following are some of the resolutions requiring special notice:
(1) Resolution to remove a director.
(2) Resolution to fill up a casual vacancy of the director.
(3) Resolution to appoint as Auditor a person other than the retiring person.
(4) Resolution to appoint as Director a person in place of removed director.
Distinction between Ordinary Resolution and Special Resolution: