The nature and purpose of advertising differ from one industry to another and lor across situations. The targets of an organisation’s advertising efforts often vary, as do its role and function in the marketing programme. One advertiser may seek to generate immediate response or action from the customer; another may want to develop awareness or a positive image for its products over a longer period.
Marketers advertise to the consumer market with national, retail/local, and direct response advertising, which may involve stimulating primary or selective demand. For business/ professional markets, they use industrial, professional and trade advertising.
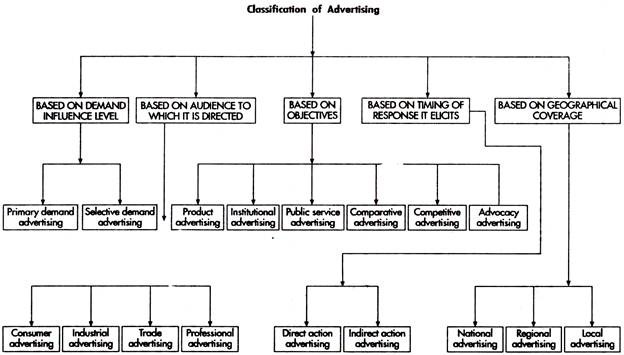
To better understand the nature and purpose of advertising to the final buyer, it is useful to examine these classifications of the various types of advertising (Table 15.1).
1. Advertising Based on Demand Influence Level:
A major portion of advertising effort is designed to increase the demand for a product or service. There are two kinds of demand: Primary and selective. Primary demand refers to the demand for the generic product such as milk, magazine, radio, television set. Selective demand is designed to gain acceptability for a particular manufacturer’s brand i.e. Onida TV.
Primary Demand Advertising:
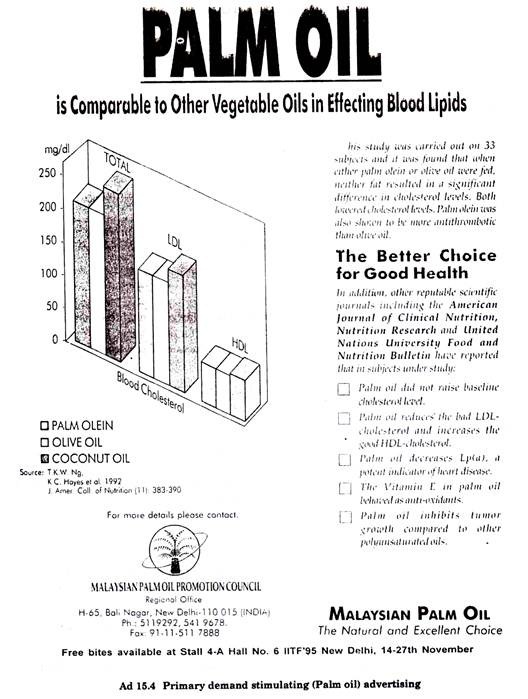
When the product is in the introduction stage, the best promotional strategy may be to use advertising that is designed to gain acceptability for a product group rather than a particular brand. Frequently primary demand advertising is conducted by an industry, group or trade association in order to promote a product. (Ad. 15.1, 15.2, 15.3, 15.4)
Selective Demand Advertising:
Relatively few completely new products appear on the market, thus most new product introductions today are accompanied by selective demand advertising, which promotes a specific manufacturer’s brand.
Most advertising for various products and services is concerned with stimulating selective demand and emphasizes reasons for buying a particular brand. Advertisers generally assume that there is a favourable level of primary demand for a product class and focus attention on increasing their market share.
2. Advertising Based on the Audience to Which it is Directed:
Consumer Advertising:
Consumer advertising is that type of advertising that is directed towards the ultimate consumers.
Industrial Advertising:
It is done by manufacturers or distributors of industrial goods and is designed to stimulate demand among the industrial buyers of such goods as raw materials, machinery, equipment, supplies or fabricated parts (Ad. 15.5).
Trade Advertising:
Trade advertising is done by manufacturers to obtain aggressive promotion and sale of manufacturer’s line of products by the wholesalers and retailers who are logical outlets for such products.
Professional Advertising:
It is targeted to the professional groups such as doctors, lawyers, engineers or professors to encourage them to use the advertiser’s product or specify it for other’s use. Professional groups are important because they constitute a market for products and services they use in their businesses.
3. Objective Based Advertising:
Product Advertising:
It is designed to promote the sale of a particular product or brand. The objective of product advertising is to promote particular products or services that the organisation sell. The marketer may use such promotion to generate exposure, attention, comprehension, attitude change or action for offering.
It may be of three types:
(a) Informative product advertising
(b) Persuasive product advertising
(c) Reminder product advertising.
Informative product advertising is meant for giving information about the product or service. This type of advertising is generally used in the introductory stage of the product life cycle (Ad. 15.6).
Persuasive product advertising is competitive type of promotion used in the growth stage of product life cycle (Ad. 15.7).
Reminder Product advertising generally adopted in the maturity stage of the product life cycle to remind the customer about its presence in the market (Ad. 15.8).
Institutional Advertising:
It is directed toward the complete institution with the aim to increase the good will of the institution rather than on a specific brand in the eyes of the customers, shareholders, employees, suppliers etc. Institutional advertising is often closely related to the public relation function of the enterprise (Ad. 15.9)
Public Service Advertising:
Public Service Advertising is designed to operate in the public interest and promote the public welfare. Public service advertisements emanates from various commercial as well as non-commercial organisations. It involves sponsoring, pollution control such public welfare activities as safe driving, good health, how to prevent epidemic etc. (Ad 15.10, 15.11, 15.12).
Advocacy Advertising:
Also called as issue advertising is concerned with the propagation of ideas and the classification of controversial social issues of public importance. In other words, it can be said to be another form of public service advertising.
It is done when a commercial or non-commercial organisation present a point of view about economic or social problems or be defensive in order to dispel existing prejudices or to correct wrong impressions about a firm or industry (Ad. 15.14, 15.15).
Comparative Advertising:
It compares specific product attributes with competitor’s brands. Today comparative advertising is used widely. Here the advertiser put the competitor’s name (sometimes not) and tell the benefits of his and competitor’s offerings. Negative comments concerning competitors are viewed as unprofessional or unethical (Ad. 15.16, 15.17).
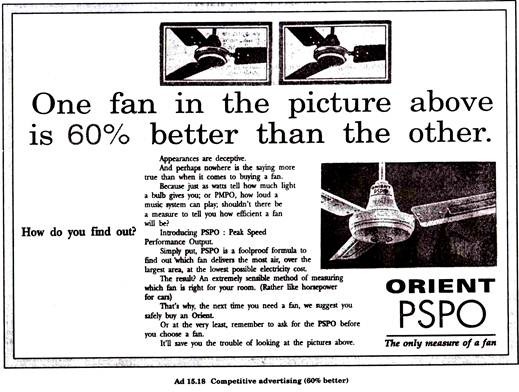
Competitive Advertising:
It focuses on stimulating selective demand within a product category. In this type of advertising the emphasis is on positioning their product on the same attributes as competitor is doing for example the advertisements of Polo and Minto, Aerial & Surf etc. (15.17, 15.18).
4. Advertising Based on Timing of Response it Elicits:
Direct Action Advertising:
Advertising designed to obtain some immediate response from the target customer is called direct action advertising. All sales promotion advertising and mail order advertising is of this type. In mail order advertising .
The seller attempts to induce the reader to mail in his order for the goods advertised. An advertisement that attempts to get the reader to send in a coupon for a sample of the merchandise would be the example of direct action advertising (15.19, 15.20).
Indirect Action Advertising:
It is designed to influence the reader to have a favourable opinion or image of the brand so that when the reader does decide to buy that product, he will buy the advertiser’s brand rather than the competing one.
5. Advertising Based on Geographical Coverage:
National, Regional & Local Advertising:
Advertising reaches people through media that are classified as national, regional or local.
National Advertising is done on nation wide scale to stimulate the demand for the product among ultimate buyers. If the advertising is confined to one region of the country, it is called as regional advertising.
Local advertising is confined to one trading area or city and sometimes called as retail advertising. This type of advertising is done by local manufacturers.