After reading this article you will learn about:- 1. Introduction to GIC 2. Membership Criteria of GIC 3. Major Activities 4. Insurance Portfolio.
Introduction to GIC:
The General Insurance Council is a statutory body under the Indian Insurance Act 1938.
Section 64 C of Part II-A of the Indian Insurance Act 1938 states that there shall be two Councils of the Insurance Association of India, namely:
a. The Life Insurance Council consisting of all the members and associate members of the Association, who carry on life insurance business in India, and,
b. The General Insurance Council consisting of all the members and associate members of the Association who carry on general insurance business in India.
The General Insurance Council is an industry body funded by contribution from member companies. There are currently 22 members of the General Insurance Council of India.
Membership Criteria of GIC:
GI Council membership is automatically extended by invitation to all insurance companies authorised to underwrite non-life insurance business of any class in India.
Role of General Insurance Council:
The General Insurance Council represents the collective interests of the Non-life Insurance companies in India. The Council speaks out on issues of common interest; helps to inform and participate in discussions related to policy formation; and acts as an advocate for high standards of customer service in the insurance industry.
General Insurance Council leads a number of initiatives by bringing together experts from its member companies, the national re-insurers and the regulator in a common forum for debating specific issues from time to time and helps resolve them in a structured fashion.
Major Activities of GIC:
a. Promotion of a better understanding of non-life insurance amongst the public:
Providing inputs to the media about the developments in the non-life insurance industry.
b. Promotion of sound development and maintenance of the reliability of the non-life insurance industry:
Developing codes of conduct for member companies, strengthening non-life insurance companies’ disclosure, developing compliance programs to observe laws and regulations, etc.
c. Presentation of requests and proposal:
Representing the non-life insurance industry in the presentation of regulatory reform requests, and of opinions to insurance administration.
d. Response to social issues:
Combating automobile theft, taking measures to prevent insurance fraud, etc.
e. International activities:
Promoting dialogue and information exchange with overseas insurance associations, participating in international organizations’ activities and international meetings.
f. Consumer Services:
The GI Council promotes consumers’ understanding of insurance, and the presence of the general insurance industry in society.
g. Social Responsibility:
The GI Council undertakes activities having far reaching social implications in association with law enforcement agencies.
i. Automobile Theft Prevention.
ii. Prevention of Uninsured Driving.
iii. Response to Fraudulent Claims.
h. Requests and Proposals:
The GI Council carries out activities to realize the establishment and revision of laws and regulations beneficial to the general insurance industry and society by making requests and proposals to the related parties.
i. Requests for Regulatory Reform.
ii. Requests for Senior Citizen Health Insurance.
iii. Opinions to Public Consultation.
i. GI Council promotes international cooperation:
Cooperation with Insurance Associations
j. Development of the Business Environment:
The GI Council supports the operation of various insurance related systems and mechanisms instrumental to insurance companies., such as Commercial Vehicles Third party insurance pool.
Insurance Portfolio of GIC:
There are so many players of insurance in the market. Once upon a time there was monopoly of LIC in the field of life insurance. In case of non -life insurance there was no dependable source unless GIC was established. With the time and liberalized policies of the Government of India the field of insurance was opened to private sectors also.
A brief state of affairs of development in insurance sector in India is:
Insurance History and players:
Insurance industry, as on 1.4.2000, comprised mainly two players: the state insurers.
Life Insurers:
Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC)
General Insurers:
A. General Insurance Corporation of India (GIC)-(with effect from Dec’2000, a National Reinsurer)
GIC had four subsidiary companies, namely (with effect from Dec’2000, these subsidiaries have been de-linked from the parent company and made as independent insurance companies.
1. The Oriental Insurance Company Limited.
2. The New India Assurance Company Limited.
3. National Insurance Company Limited.
4. United India Insurance Company Limited.
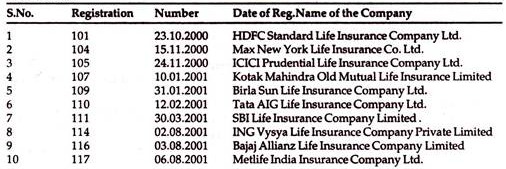
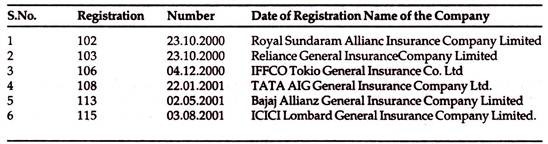
Yr: 2000-2001: (From 2nd April ‘2000 to 31st December’2001)
Insurance Industry in the year 2000-2001 had 16 new entrants, namely:
Life Insurers:
General Insurers:
Yr: 2001-2002: (From 1st Tan 2001 to Dec. 2002)
Insurance Industry in this year, so far has 5new entrants; namely
Life Insurers:
General Insurers:
Yr: 2003-2004: (From 1st Jan 2003 till Date)
Insurance Industry in this year, so far has 1new entrants; namely
Life Insurers:
Yr: 2004-2005:
Insurance Industry in this year, so far has 1new entrants; namely
Life Insurers:
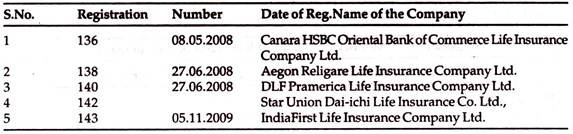
Yr: 2006-2007:
Insurance Industry in this year, had 1new entrants; namely
Life Insurers:
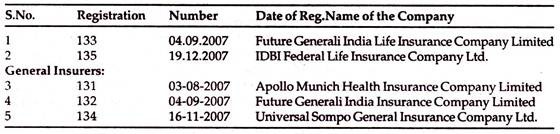
Yr: 2007-2008:
Insurance Industry in this year, had 5 new entrants; namely
Life Insurers:
Yr: 2008-2009:
Insurance Industry in this year, so far has 3 new entrants in Life and 1 new entry in General; namely
Life Insurers:
General Insurers: