In this article we will discuss about:- 1. Meaning of SCBA 2. Commercial and SCBA Computations: Distinction 3. Social Desirability of a Project.
Meaning of SCBA:
The economic analysis in project appraisal for evaluating investment projects an important consideration is the analysis of social cost and benefits. In this analysis, the direct economic benefits and cost of the project on distribution of income in society, level of savings and investments in society, the contribution of the project towards fulfilment of certain merit-wants (e.g. employment, social orders, self-sufficiency etc.) are analysed.
Thus SCBA is also referred to as economic society benefit analysis, is a part of the economic analysis in project appraisal. It is a methodology developed for evaluating investment projects from the point of view of the society (or economy) as a whole.
SCBA is used primarily for evaluating public investments and has received increased emphasis in recent years due to the growing importance of public investments especially in developing countries where government play significant role in economic development. SCBA is also relevant in major private investments, which require governmental approval since these investments have bearing on national considerations.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In modern times, all project investments have impact on society and nations economy.
As such doing SCBA is to subject project choice to a consistent set of general objectives of national policy, such as:
1. Choices of project in the context of total national impact.
2. Evaluation of total impact in terms of consistent and appropriate set of objectives having bearing on nations economy and on society.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
3. Correlation to national planning.
4. Consequences on employment and output.
5. Consumption, savings, Foreign exchange earnings, income etc.
6. Distribution and relevant things to national objectives.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
For the purpose of SCBA all the costs must be expressed in terms of shadow prices, by subtracting transfer payments, such as taxes, duties from the financial costs and benefits. This is possible by applying the shadow exchange rate before converting costs into shadow prices.
It is important to identify all direct and indirect economic costs both tangible and intangible as well as benefits to assure a fair and reasonable choice of project and to assure its effective implementation. The same applies to non-quantifiable, intangible costs and benefits. The most obvious are environmental and social costs and benefits, though institutional, political and others are often also not insignificant.
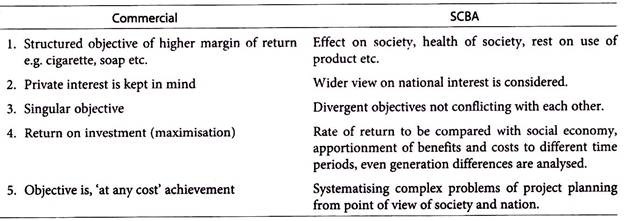
Commercial and SCBA Computations: Distinction:
The basic difference between Commercial and SCBA computations in project appraisal lies in the following:
Social Desirability of a Project:
A project is also assessed from the social angle in addition to assessment of its commercial viability.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The following social desirability factors will be considered in accept or reject decisions of a project:
1. Employment Potential:
The employment potential of a project is looked into. A project with high employment potential is considered highly desirable.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. Foreign Exchange:
A project with potential to earn foreign exchange to the country or an import substitution project which saves the country’s foreign exchange reserves is highly desirable.
3. Social Cost-Benefit Analysis:
A project with net benefits to the society over the costs to the society is preferred.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
4. Capital-Output Ratio:
If the value of expected output in relation to the capital employed is high, the project is given priority over the others.
5. Value Added Per Unit of Capital:
The amount invested in the project should generate the value addition to the capital employed by earning surplus profits which can be used for further capital investments to contribute development of the national economy.