Some frequently asked exam questions on strategic management are as follows:
Q.1. Write a short note on strategic decision making framework.
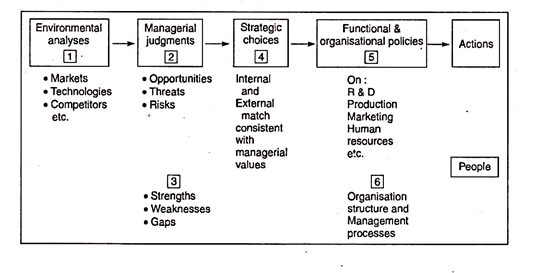
Ans. The widely accepted framework for making strategic decisions may be illustrated as under :
Typically, it urges managers to proceed sequentially through the following logical steps :
1 Analyse the environment,
2 Form broad judgments by synthesizing information about SWOT,
3 Make strategic choices,
4 Evolve policies that reinforce strategic choices, and
5 Implement these policies by motivating people.
Q.2. Distinguish between strategy and tactics.
Ans. Strategy includes a plan for deploying resources to establish a favorable position. Tactics are schemes for specific actions, typically oriented more toward the short term. Tactics are the specific activities undertaken to assure success of the strategies. The tools of strategy include product design and attributes, as well as pricing, promotion, and distribution of the product.
A strategy may involve investing heavily in promotion to increase marketing effectiveness or lowering prices to build volume and increase market share with specific segments of the market. Tactics used to accomplish this strategy include the advertising message, the media choice, and the frequency of the advertising.
Q.3. Give an outline of relation between ‘Strategy and Customer’ in brief.
Ans. A company with no strategy is likely to lose its competitiveness. The essence of good strategy making is to build a strong market position and a capable organisation to create the customers to whom the company wants to appeal. Foremost is the need to create a customer, which essentially means identifying needs in the marketplace and developing an offering to convert potential buyers into customers.
Q.4. Explain in brief the concept of strategic thinking.
Ans. Strategic thinking is concerned with outdoing an adversary, knowing that the adversary is trying to do the same to a person or a firm in particular. Strategic thinking provides better guidance to the firm regarding what the company is trying to achieve or accomplish.
Analysis is the critical starting point of strategic thinking, and assessment becomes one of the primary concerns for it.
The conceptual approach of strategic thinking, thus, includes the dimensions like SWOT analysis.
Q.5. Establish a relationship between ‘Strategic Directions’ and ‘Vision’ of a company.
Ans. Companies rising to prominence in their markets pursue strategic directions relentlessly. A first step is to have a strategic direction that refers to the network of vision, goals, and objectives. A company can expect to achieve a competitive advantage or leadership position only when it has laid out its strategic direction. The success of every company is based on a direction, preferably long-term, that differentiates the company’s approach from that of others.
A vision determines what the company should work toward, in the light of long-range opportunity. A company’s strategic vision constitutes the activities that the company intends to pursue in creating its customers. To make a vision explicit and action-oriented, many companies have adopted what is known as a “mission statement,” which defines the goals, values, and overall direction of the company.
L & T’s ‘vision’ given below highlights a relationship between it and its ‘strategic directions’:
Q.6. What is planning?
Ans. Planning is ‘deciding in advance what to do, how to do it, when to do it and who is to do it’.
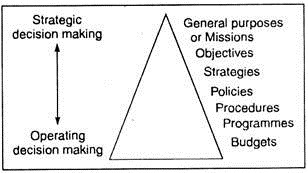
In any organisation there is a ‘hierarchy of plans’ and such hierarchy of plans corresponds to the hierarchy of authority and to the kinds of decision making that occur at different levels (diagram below):
Thus, planning involves a system of objectives that are needed to be achieved by the plans, and which can be used to evaluate alternative courses of action (that are identified by the planning process) in order to make a choice of a decision, be it operating or strategic.
The main aspects of planning are that it precedes all other management functions and that it is pervasive in terms of the detail, the time horizon, and the scale of resources involved.
Q.7. What are the basic elements of planning?
Ans. Any plan involves the following elements:
(a) Setting of ‘objectives’;
(b) Identification of ‘tasks’ to achieve these objectives;
(c) Allocation of ‘resources’ after identifying them;
(d) Determination of ‘interdependence’ between tasks, resources and performance ‘sequence’;
(e) ‘Coordination’ of activities for maximising achievement of objectives at minimum cost; and
(f) ‘Implementation’ of the plan by communicating its requirements to those concerned and by establishing ‘control’ procedures.